Understanding Metric Measurements in Science
260 likes | 370 Vues
Learn the basics of metric measurements including length, mass, volume, temperature, density, and time. Understand how to convert between units, read measurements, and calculate volume of solids and irregular shapes. Practice scientific notation and metric conversions.

Understanding Metric Measurements in Science
E N D
Presentation Transcript
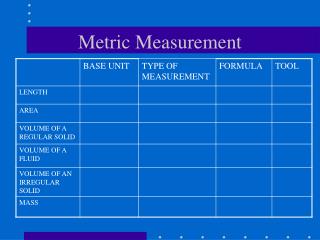
Types of Metric Measurement • Length • Mass • Volume • Temperature • Density • Time
Length • Distance between 2 points • Basic Unit: meter (m) • Equipment: meter sticks, metric rulers
Mass • Amount of matter in an object • Basic Unit: gram (g) • Equipment: Triple Beam Balance ** Weight is different than mass! Weight is mass x force of gravity. Mass is constant. Weight can change.
Volume of liquids Basic Unit: liter (l) Equipment: graduate cylinder *Always read a graduate cylinder at eye level. Meniscus- curved upper surface of a column of liquid.
Volume of Liquids-cont. • Read the volume using all certain digits and one uncertain digit. • Certain digits determined from marks on cylinder • Uncertain digit is estimated. Volume: 6.62 ml
Volume: 11.5 ml Volume: 52.7 ml
Volume of Solids • Basic Unit: cm3 • Equation: • V = L x W x H • Example: V= 3cm x 3cm x 3cm 3 cm 3 cm 3 cm
Volume of Irregular Solids • You will use a graduate cylinder by water displacement.
Temperature • The measure of how hot or cold something is. • Basic Unit: Kelvin (K) • Equipment: Thermometer • Most scientists use Celsius (C°)
Density • Closeness of particles(how spread apart they are) • Mass per unit volume of an object • Basic Unit: grams per cm cubed (g/cm3) • Equation: D = M / V
Time • Interval between 2 events. • Basic Unit: Seconds (sec) • Equipment: Clock or stopwatch
Metric Conversions Going Up: Move the decimal point left for every step you take. Kilo 1000 Hecto 100 K Deka 10 H Base Unit 1 Dk Deci 0.1 g , l, m Centi 0.01 d Going down: Move the decimal point right for every step you take. Milli 0.001 c m
Metric Conversions Going Up: Move the decimal point left for every step you take. Kilo Hecto K Deka H Base Unit Dk Deci g ,l, m Centi d Going down: Move the decimal point right for every step you take. Milli c m
Converting Metric Units Practice Problem 1: 1000 mg=______g Practice Problem 2: 160 cm=_______ mm Practice Problem 3: 109 g=________kg
Converting Metric Units Compare using >, <, or =. Problem 4: 56 cm 6 m Problem 5: 7 g 698 mg
Metric Conversion: Answers Problem 1:1 g Problem 2: 1,600 mm Problem 3: .109 kg Problem 4: < Problem 5: >
Conversion Practice Problems • 27 Dkm = ______________ cm • 2, 437 cm = ______________ km • 14 kg = __________________cg
Fri. Practice Problems • 65 dg = ______________Dkg • 100,000 mm = _______________ km • Find the volume of this object. (Each small block is 1 cm long)
Practice Problems Answers • 0.65 Dg 2) 0.1 km 3. 27 cm3
A shorter way to write very large & small numbers. Example: 300,000,000 m/s (speed of light) = 3.0 * 108 Coefficient Exponent Scientific Notation To write a number in scientific notation: 1. Put the decimal after the first digit and drop the zeroes 2. Count the number of places from the decimal to the end of the number.
Example 1: 123,000,000,000 Coefficient = 1.23 In 123,000,000,000 there are 11 places. Exponent = 11 Answer : 1.23 * 1011 Example 2: 0.000001 s Coefficient= 1.0 In 0.000001 there are 6 places. Exponent: 6 Answer: 1.0 * 10-6 s
Scientific Notation Practice Problem 1: 1,000 000 km = 1.0 * 106 km Practice Problem 2: 5, 600, 000, 000, 000, 000, 000, 000 m/s = 5.6 *1021 m/s Practice Problem 3: .311 000 000 000 000 L = 3.11 * 1014 L