Understanding Color: The Science of Light, Models, and Perception
230 likes | 379 Vues
This text explores the fundamentals of color perception and production through light. It explains how the human eye sees light as electromagnetic waves and discusses the concepts of pigment, color models, and the RGB/CMYK systems. The document delves into the terms 'gamut,' 'hue,' 'saturation,' and the distinctions between additive and subtractive color. Further, it describes color wheels, complementary colors, and their psychological effects, offering insights into how color interacts in art and design, making it relevant for artists and designers alike.

Understanding Color: The Science of Light, Models, and Perception
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Visible Light • The human eye sees light. • Light is really a very fast electromagnetic wave. • A wave is a sinusoidal repeating curve • One nanometer (one billionth of a meter) = 10 Angstrom
What is Pigment • from Latin pigmentum, from pingere, to paint. • A setting used as or for coloring
What is a Model? • An abstraction of reality • A schematic description of a system that accounts for its properties • A color model determines how pigments combine to produce color
What is a Gamut? • A complete range or extent • Origin was musical instruments, meaning the range of notes an instrument makes. • So, it is the range of color available in a particular color space
Hue Saturation • A single visible color, ranging from red through yellow, green, and blue, determined by the dominant wavelength of the light • The amount of gray in a particular color. More gray is less saturated, while a bright color, one with very little gray in it, is saturated
What is a Shade is the mixture of a color with black, which reduces lightness
What is a Tint is the mixture of a color with white, which increases lightness
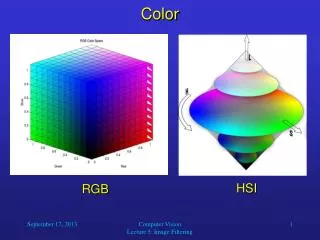
HSB Model • Based on the human perception of color • HSB stands for Hue, Saturation, Brightness • HSB model can be used to define a color on the Color palette or in the Color Picker dialog box • HSB is not usually a choice for creating or editing images
L*a*b Model • Based on one luminance (lightness) component and two chromatic components • Largest number of colors available with greatest precision • Create all colors contained by other color models • Device-independent: colors will not vary, regardless of hardware
What is a mode? • Mode is the manner, way, or method of doing something • Example: • Transportation mode: Car, Bus, Train, Plane • RGB 24 bit Color Mode • Red, Green, and blue each have 8 bits (28) for a total of 24 bits = 16,777,216 possible (224) colors
Color Mode • L*a*b Mode • HSB Mode • RGB Mode • CMYK Mode • The color mode is used to determine which color model will be used to display and print an image
Additive Color • Beams of colored light are mixed to form other colors. • No lightis BLACK • All lightis WHITE
RGB • RGB is Red,Green,Blue • Based on Light (Additive) Color • 3 Primary lights’ brightness are combined to create a color • Color range is based on number of steps each light’s brightness can have. • Used for video and screen presentation
Subtractive Color • When Light passes through a color filter, or reflected off a color surface, certain wavelengths are absorbed and others transmitted • All Colors absorbedis BLACK • No Color absorbedis White Magenta Yellow Cyan
CMYK • CMYK is Cyan,Magenta,Yellow,blacK • Based on Reflected (Subtractive) Color • Dots of color are combined to create color in a Process • The process used and the size of the dot determine the resolution of the picture. • Used in printing
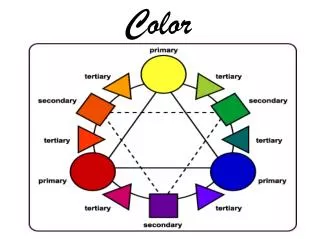
Color Wheels • A circular chart that shows primary and secondary colors. CMY for printing RGB for Computers Primary colors: 3 colors at 60°, 180°, and 300°. Secondary colors: created using adjacent primary colors. 0°, 120°, and 240°. Tertiary color: created by using adjacent primary and secondary colors. 30°, 90°, 150°, 210°, 270°, 350°.
Color Wheels • Older RYB Color Wheel • Still widely used Red, Yellow and Blue are used as primary colors.Orange, Green and Purple are secondary colors.
Analogous Colors • A palette of compatible color combinations that blend well together. • Neighbors on the color wheel.
Complementary Color • Colors opposite each other on the color wheel • They contrast, enhance and intensify each other. • Complementary colors need to be used with caution.
Triadic Colors • Three colors, 120° apart on the color wheel. • High-Energy colors • Work well together • Often used in logos