Acceleration
100 likes | 225 Vues
Acceleration is a vector quantity representing the rate of change of an object's velocity. It's often misunderstood in everyday language but is crucial in physics. An object accelerates when its velocity changes, which can occur at a constant rate. This unit explores average acceleration, defined mathematically, and the units used such as m/s² and km/hr/s. Additionally, we discuss how acceleration is represented in graphs, where the slope indicates the rate of acceleration. This foundational concept is essential for understanding motion in physics.

Acceleration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Acceleration unit 6.2 year 10
Introduction • An often confused quantity, acceleration has a meaning much different than the meaning associated with it by sports announcers and other individuals.
Acceleration • Acceleration is a vector quantity that is defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity • An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity.
Acceleration • Teacher demonstration • As an object fall it accelerates due to the force of gravity.
Constant acceleration • Sometimes an accelerating object will change its velocity by the same amount each second. This is referred to as a constant acceleration since the velocity is changing by a constant amount each second.
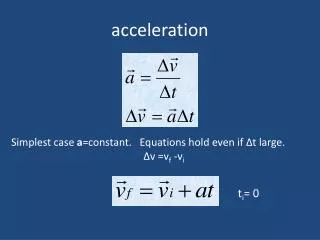
Calculating the Average Acceleration [ vav] • The average acceleration (a) of any object over a given interval of time (t) can be calculated using the equations
Symbols • Δ is the letter Delta from the Greek alphabet. It means a change in. • Example: Δt = a change in time
Units • Acceleration values are expressed in units of velocity/time. Typical acceleration units include the following: • m/s/s • km/hr/s • ms-2 • m/s2
Acceleration and graphs High acceleration is a rapid increase in speed. The speed–time graph would be a steeper one than if you accelerated at a lesser rate; that is, the slope or gradient of a speed–time graph gives us the rate of acceleration.
Animation • Direction of Acceleration and Velocity