Understanding Digitizing Errors in GIS: Types, Examples, and Their Impacts
90 likes | 224 Vues
Digitizing errors in Geographic Information Systems (GIS) can lead to significant inaccuracies. Common types include overshooting, undershooting, and issues like polygons not closing or missing data. For instance, improperly digitized rivers may flow in the wrong direction, creating unrealistic landscape features. Errors can occur in location accuracy, edge matching, and more. Recognizing and correcting these errors is essential for seamless mapping and reliable analysis, ensuring that contour lines never cross and polygons represent real-world boundaries accurately.

Understanding Digitizing Errors in GIS: Types, Examples, and Their Impacts
E N D
Presentation Transcript
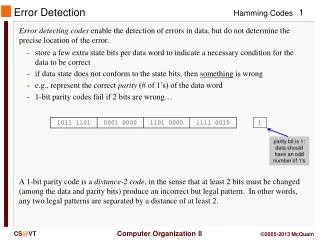
Types of errors • Digitizing errors • overshooting • undershooting • polygons do not close • missing data
Contour lines never cross!! An example of horrible digitizing!!!
overshooting “dangling” node
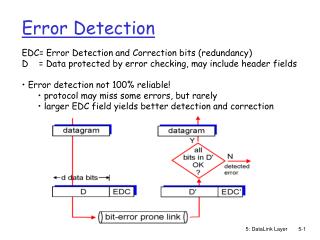
River digitized in the wrong direction
Digitizing rivers in the wrong direction creates “canyon” -like features instead of river valleys 3900 m 3500m
Types of errors • Location errors (x,y coordinates) • Edge matching (“seamless”)