Modeling the Dynamics of a Bouncing Ball and Optimization Techniques in Linear Programming
60 likes | 203 Vues
This study explores the dynamics of a bouncing ball, detailing its motion as it falls, bounces, and comes to rest. We aim to generate data on the maximum height reached after each bounce while neglecting air resistance. The mathematical model includes the coefficient of restitution and equations governing the ball's kinetic energy before and after each collision. Additionally, we examine optimization, using linear programming to maximize profitability for businesses under specific constraints, and introduce Excel Solver as a tool for solving these optimization problems.

Modeling the Dynamics of a Bouncing Ball and Optimization Techniques in Linear Programming
E N D
Presentation Transcript
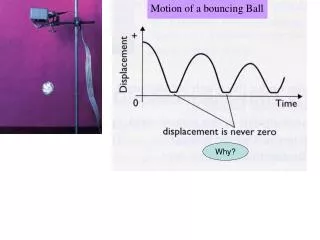
Model of a Bouncing Ball A ball falls from a height, bounces against a surface, and jumps to the air again. This repeats a number of times until the ball rests on the surface.
Model of a Bouncing Ball • Objective • Generate data showing the maximum height reached by the ball after each bounce and plot them • Assumptions • Air resistance is negligible (the speed of the ball is not very high) • The surface is a smooth plane, perpendicular to the falling ball and rigidly attached to an object massively larger than the ball Mathematical Model h = The height from which the ball drops h’ = the new height that the ball bounces back to after hitting the surface k = Coefficient of restitution (a measure of the elasticity of the collision) k=1 for perfect elastic collision, k<1 otherwise According to the theory of collisions: Kinetic energy after collision = k× kinetic energy before collision mv2after = k∙mv2before (Eq. 1) mv2after = mghn (Eq. 3) mv2before = mghn-1 (Eq. 2) hn = khn-1 (Eq. 4)
Optimization • What is Optimization • Its objective is to select the best possible decision for a given set of circumstances without having to enumerate all of the possibilities • Involves maximization or minimization as desired • How can a large drug company determine the monthly product mix at their Indianapolis plant that maximizes corporate profitability? • If Microsoft produces Xbox consoles at three locations, how can they minimize the cost of meeting demand for Xbox consoles? • Linear Programming • To optimize a linear objective function, subject to linear equality and inequality constraints • A constraint is a condition that a solution to an optimization problem must satisfy
Maximize z = 15x1+10x2 subject to 0≤x1 ≤2, 0 ≤ x2 ≤ 3, x1+x2 ≤4 The objective function is z = 15x1+10x2 The constraints are: 0≤ x1≤2, 0 ≤ x2≤ 3, x1+x2 ≤4
x1=2 x2=3 Optimal point (x1=x2=2) x1+ x2 = 4 z = 40 z = 30 z = 20 z = 10 x2 Feasible Region x1 zmax = 15*2 + 10*2 = 50
Excel Solver • A Microsoft Excel Add-In • Go to Tools >>Add-Ins , select Solver Add-in, click OK • Originally designed for optimization problems but also useful for root finding and similar mathematical problems • Target cell • The objective or goal • Maximize, minimize or set a specific value to the target cell • Changing cells • Can be adjusted until the constraints in the problem are satisfied and the cell in the Set Target Cell box reaches its target • Constraints • The restrictions placed on the changing cells