Fermentation
70 likes | 237 Vues
Fermentation. Cellular Respiration. The respiration that we’ve discussed to this point has all relied on oxygen There are several types of respiration that can occur without oxygen These methods still rely on glycolysis to produce ATP, but create different waste products. O 2.

Fermentation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cellular Respiration • The respiration that we’ve discussed to this point has all relied on oxygen • There are several types of respiration that can occur without oxygen • These methods still rely on glycolysis to produce ATP, but create different waste products
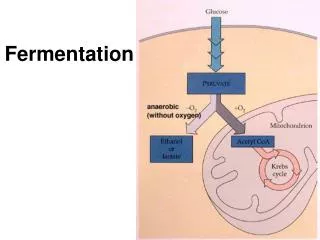
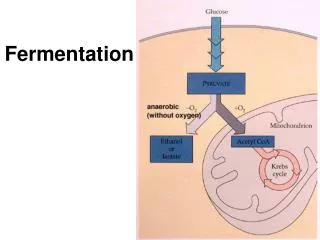
O2 What if oxygen is missing? • No oxygen available = can’t complete aerobic respiration • Cells can undergo: • Anaerobic respiration (also known as fermentation) • 2 Types: • alcohol fermentation • lactic acid fermentation • no oxygen or no mitochondrianecessary (think bacteria) • can only make very little ATP • large animals cannot survive long term using fermentation yeast bacteria
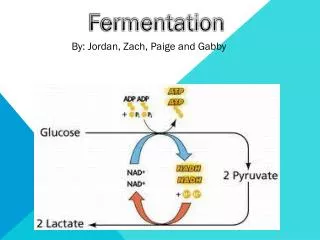
O2 Anaerobic Respiration • lactic acid fermentation • bacteria, animals • bacteria make yogurt • animals feel muscle fatigue • glucose ATP + lactic acid
Lactic acid fermentation Glucose->pyruvic acid -> 2ATP 2 lactic acid GLYCOLYSIS FERMENTATION used to make cheese and yogurt ~ in humans during strenuous exercise not enough oxygen from blood “oxygen debt” ~ lactic acid accumulates in muscle; leads to fatigue and pain Will be converted back to pyruvic acid in liver
O2 Anaerobic Respiration • alcohol fermentation • yeast • make beer, wine, bread • glucose ATP + CO2+ alcohol
Alcoholic fermentation glucose -> pyruvic acid-> 2 ethyl alcohol + 2 CO2 2ATP GLYCOLYSIS FERMENTATION • used by yeast cells and some bacteria to produce ATP, CO2and ethyl alcohol