Understanding Natural Monopoly Regulation: Goals and Challenges
60 likes | 181 Vues
The regulation of natural monopolies aims to replicate competitive market outcomes, ensuring fair and just rates for consumers. Key regulatory goals include affordability, universal service, and supporting economic development. However, challenges arise due to barriers to entry, uncertainty about costs, and imperfect information. Unlike competitive industries, natural monopolies can achieve productive and allocative efficiency as economies of scale reduce average costs significantly depending on production volume. This document discusses the fundamental principles and specific policies governing natural monopolies, highlighting the complexities regulators face.

Understanding Natural Monopoly Regulation: Goals and Challenges
E N D
Presentation Transcript
ECO 435 – Natural Monopoly Problem David Loomis
Fundamental Goal of Regulation • To mimic a competitive market outcome even when the underlying market is not competitive • “other goals” • Fair and just rates • Specific policies regulators believe to be in customers’ best interests • Universal service • Affordability • Economic development
Competitive Ideal • Maximizes the sum of consumer and producer surplus • Productive and allocative efficiency
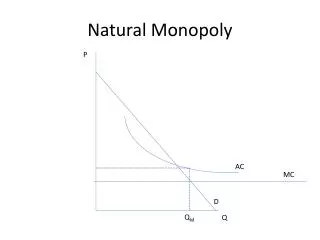
Factors that Preclude a Competitive Outcome • Natural Monopoly • Firms builds pipeline costing $365 million with capacity of 1 million cubic meters; has to repay $36.5 million/yr • If it transports 100 cubic meters per day, AC=$1,001/cubic meter • If it transports 1,000 cubic meters per day, AC=$101/cubic meter • Also AC of building pipe decreases as size of pipe increases/cost=circumference, production=volume • Barriers to entry
Other Complicating Factors • Uncertainty about costs – imperfect information • Other regulatory interventions – Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) – increasing costs
B&T 2.1, 2.2 and 2.5 • See Notes