Photosynthesis
330 likes | 391 Vues
Learn about photosynthesis, its importance, the parts of plants involved, photosynthetic pigments, light reaction, dark reaction (Calvin cycle), and the chemical equation. Discover how autotrophs convert sunlight into energy, the role of chloroplasts, and the significance of photosystems. Explore the work of scientist Melvin Calvin in advancing our understanding of this vital process.

Photosynthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Photosynthesis By Dr. Huq
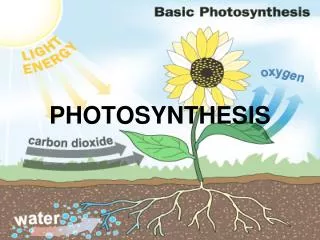
Photosynthesis • Photosynthesis concept. The process by which autotrophs convert sunlight to a usable form of energy is photosynthesis
What is the equation for the chemical reaction of photosynthesis?
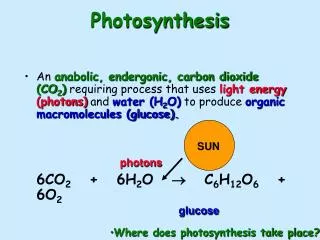
What is the equation for the chemical reaction of photosynthesis? Six molecules of carbon dioxide react with six molecules of water to form 1 molecule of glucose and six molecules of oxygen.
Why is this important to us? We cannot make our own food (glucose, energy), we must get our food from plants. Plants are the first step in the food chain.
Why is this important to us? The oxygen released during photosynthesis is necessary for all living things.
Photosynthesis • AUTOTROPH. An organism that produces its own food from inorganic (carbon dioxide) compounds and sunlight.
What Parts Of The Plants Are Involved In The Process Of Photosynthesis?
Chloroplast • Chloroplast--A plastid that contains chlorophyll and is the site where photosynthesis and starch formation occur.
Photosynthetic pigments • Most of the pigments in green plants are bound to the trimeric light-harvesting complex II (LHCII). It is located at several positions in photosystem II, but also at other locations. It is very important for the organization of the thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts and for the separation of photosystems I and II.
Photosynthetic Pigments • Certain pigments in autotrophs are essential for photosynthesis. The most common and important of these photosynthetic pigments is called chlorophyll.
Photosynthetic Pigments • Chlorophyll a is the major pigment. However chlorophyll b & Beta carotene are two accessory pigments for photosynthesis.
What Color Of Light Is Needed? chlorophyll which absorbs red and blue light (and appears green) and carotenoids which absorb in the blue (and appear yellow).
Where these reactions take place? Reactions occur in different areas of the thylakoid called photosystem I & photosystem II
What are photosystems? Inside the Thylakoids, hundreds of chlorophyll molecules & other pigments are organized into units called photosystems. These are light collecting units of chloroplast.
Besides light and the organelle, what else is used in this process? H2O And CO2
What is Light reaction? PhotosystemII uses sunlight to split water into H+,energized electrons and O2. Most of the Oxygen diffuses out into the air. The electrons enter the electron transport chain
Electron transport Systems ATP = Adenosin triphosphateADPATP NADPH = Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide phosphate NADP NADPH
Then what Happens in Light Reaction? • Electron transport: Energized electrons are shuttled from Photosystem II by carrier molecules. The carrier molecules use the electron’s energy to actively transport H+ from the stroma into the thylakoid space
What is next in Light Reaction ? • Photosystem I. Using sun’s energy the • energy- depleted electrons are reenergized in Photosystem I. The energized electrons are used to produce NADPH, (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide phosphate) a molecule that will later be used to make glucose.
What next in light Reaction ? • ATP synthesis: The high H+ concentration in the thylakoid space creates a concentration gradient. H+ difuses back into the stroma through an enzyme, ATP synthase. The energy released by the flow of H+ converts ADP to ATP
What is Dark reaction? • The Calvin cycle follows light-dependent reaction. It takes place in the stroma. It uses NADPH ,ATP (Adenosin triphosphate) and H+. It needs CO2 to make sugar. 6 molecules of CO2is used to make one molecule of Sugar. However one molecule of CO2is processed at a time
What is Step 1 of Dark Reaction? • Carbon Fixation: For each glucose molecule , 6 molecules of CO2 reacts with6 molecules of five carbon sugar RuBP (Ribulose 1,5 phosphate). The result is 12 molecules of 3 carbon PGA(3-Phosphoglyceric Acid). Only one CO2 goes through the Calvin cycle at a time.
What happens in Step 2? • Production of G3P: Each molecule of PGA is converted to G3P, using energy from ATP and hydrogen from NADPH. Two G3P molecules can be combined to form glucose in other cellular process.
And in Step 3 of Calvin Cycle? • Restoring RuBP: The other ten G3P molecules are recycled back to RuBP. This requires energy from 6 ATP. RuBP is used in the next turn of the Calvin cycle.
What are the products of this process? What is the Chemical reaction?
Chemical reaction6CO2 + 6H2O light enegry & chlorophyll C6H12O6 + O2
Name of the scientist: Melvin Calvin