Osmosis
100 likes | 285 Vues
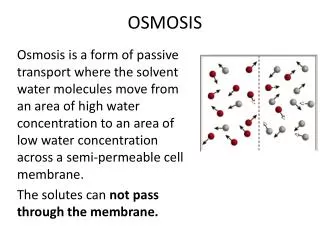
Osmosis. Movement of Water across the Cell Membrane. Let’s review diffusion!. Diffusion requires NO ENERGY Molecules move from HIGH to LOW Downhill!!!! Let’s see! Osmosis: Movement of WATER from an area of more water ( H ) to an area of less water ( L )

Osmosis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Osmosis Movement of Water across the Cell Membrane
Let’s review diffusion! • Diffusion requires NO ENERGY • Molecules move from HIGH to LOW • Downhill!!!! Let’s see! • Osmosis: • Movement of WATER from an area of more water (H) to an area of less water (L) • Water moves OPPOSITE of other molecules!
How does osmosis work? • Across a SEMI-PERMEABLE membrane • Only certain molecules, like water, can move freely across the membrane • Water molecules move from HIGH to LOW • They want to BALANCE OUT a solution • Therefore, water moves OPPOSITE of other molecules
Example of Osmosis #1 • Condition #1: More Water outside of cell • Inside cell = 98% Water, 2% salt • Outside cell = 100% Water, 0% salt 98% L Water moves into cell, salt moves out to balance CELL SWELLS or BURSTS! 100% H
Example of Osmosis #2 • Condition #2: More water inside of cell • Inside cell: 98% Water, 2% Salt • Outside cell: 95% Water, 5% Salt 98% H Water moves out of cell, salt moves in to balance 95% L CELL SHRIVELS!
Osmotic Pressure • Cells behave differently when placed in different solutions! • This is due to OSMOSIS! • Most cells are ~ 98% water! • Three types of osmotic pressure: • Hypotonic • Hypertonic • Isotonic
Hypotonic Condition • Cell is placed in 100% water • Solution outside of cell has MORE water, less of other materials (i.e., salt) • Therefore, solution is below strength (hypo) CLICK HERE FOR DEMO! 100% Water ENTERS cell 98% CELL SWELLS!
Hypertonic Condition • Cell is placed in 95% water • Solution outside of cell has LESS water, more of other materials (i.e., salt) • Therefore, solution is above strength (hyper) CLICK HERE FOR DEMO! Water LEAVES cell 95% 98% CELL SHRINKS!
Isotonic Condition • Cell is placed in 98% water • Solution outside of cell has SAME water, same amount of other materials (i.e., salt) • Therefore, solution is equal strength (iso) Water moves equally; Equilibrium exists 98% CELL STAYS THE SAME! 98%