Basic UNIX Commands
520 likes | 919 Vues
Basic UNIX Commands. Faisal Akkawi akkawi@cs.iit.edu Department of Computer Science Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, IL 60616. Topics. Handling Files and Directories Text Editors Compiling and Linking Handling Processes Archiving and Compressing Files Other Useful Commands.

Basic UNIX Commands
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Basic UNIX Commands Faisal Akkawi akkawi@cs.iit.edu Department of Computer Science Illinois Institute of Technology Chicago, IL 60616 Basic UNIX Commands
Topics • Handling Files and Directories • Text Editors • Compiling and Linking • Handling Processes • Archiving and Compressing Files • Other Useful Commands Basic UNIX Commands
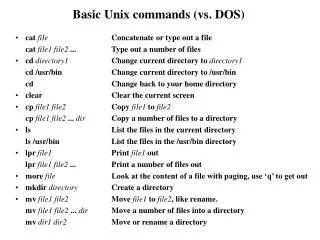
Handling Files and Directories • ls : list files • cp : copy files • mv : move files • rm : remove files • mkdir : make directories • cd : change directories • rmdir : remove directories • pwd : print working directory • chmod : change permission mode • umask : set file-creation mode mask Basic UNIX Commands
ls command • Syntax • ls [-Options] [name ...] • Description • Lists contents of directory. • Frequently Used Options • -a List all entries, including . and .. • -d Do not list contents of directories • -l Long listing • -F Mark directories with a '/', etc. • Examples • ls -alF Basic UNIX Commands
cp command • Syntax • cp [-Options] file1 [file2 ...] target • Description • File1 is copied to target. • Frequently Used Options • -f Force remove existing file • -i Ask before removing existing file • -r Copy directory trees • Examples • cp p1.c p2.c • cp p1.c p2.c mydir Basic UNIX Commands
mv command • Syntax • mv [-Options] file1 [file2 ...] target • Description • File1 is moved to target. • Frequently Used Options • -f Removes existing files without prompting the user • -i Asks before removing existing file • Examples • mv p*.c mydir Basic UNIX Commands
rm command • Syntax • rm [-f] [-i] file . . . • rm -r [-f] [-i] dirname . . . [file . . .] • Description • Removes files or directories. • Frequently Used Options • -f Removal of files without prompting the user • -i Interactive removal • -r Recursive removal • Examples • rm -f p*.o • rm -r mydir Basic UNIX Commands
mkdir command • Syntax • mkdir [-m mode] [-p] dirname . . . • Description • Creates the specified directories. • Options • -m Specifies the mode to be used • -p Create missing intermediate directories • Examples • mkdir -m 700 letter • mkdir abc • mkdir -p ./abc/def/ghi Basic UNIX Commands
cd command • Syntax • cd [directory] • Description • Change working directory. • If directory is not specified, the value of shell parameter $HOME is used as the new working directory. • Examples • cd • cd ./abc/def/ghi • cd .. Basic UNIX Commands
rmdir command • Syntax • rmdir [-p] [-s] dirname . . . • Description • Removes directories. • Options • -p Remove the directory dirname and its parent directories which become empty. • -s Suppress the message when –p is in effect • Examples • rmdir letter Basic UNIX Commands
pwd command • Syntax • pwd • Description • Prints the path name of the working (current) directory. • Examples • pwd Basic UNIX Commands
chmod command • Syntax • chmod [-R] mode file ... • chmod [-R] [ugoa]{+|-|=}[rwxXstl] file ... • Description • Changes the permissions mode of a file or directory. • Examples • chmod 444 file1 • chmod ugo+rw p*.c • chmod 700 mydir Basic UNIX Commands
umask command – I • Syntax • umask [ooo] • Description • Sets file-creation mode mask to ooo. The three octal digits refer to read/write/execute permissions for owner, group, and others, respectively. • The value of each specified digit is subtracted from the corresponding ‘digit’ specified by the system for the creation of a file. • If ooo is omitted, the current value of the mask is printed. Basic UNIX Commands
umask command – II • Examples • umask 022 removes group and others write permission (files normally created with mode 777 become mode 755; files created with mode 666 become mode 644). Basic UNIX Commands
Text Editors • pico - Simple, easy-to-use text editor • vi - Text editor based on an underlying line editor ex • emacs - Powerful and extensible - Hard to learn Basic UNIX Commands
pico • Layout is very similar to the pine mailer Basic UNIX Commands
vi • vi Modes: • Command mode : Normal and initial mode. Other modes return to command mode upon completion. ESC (escape) is used to cancel a partial command. • Input mode : Entered by setting any of the following options: a A i I o O c C s S R . Arbitrary text may then be entered. Input mode is normally terminated with ESC character. • Last line mode : Reading input for : / ? or !.Terminates by typing a carriage return Basic UNIX Commands
Compiling and Linking • cc - C compiler - Default behavior is ANSI/ISO C • make - Allows programmer to maintain, update, and regenerate groups of computer programs. Basic UNIX Commands
cc command – I • Syntax • cc [-Options] ... file ... • Description • *.c are assumed to be C source programs. • *.o are compiled object files. • a.out is the default output program name. • Frequently Used Options • -c Produce an object file • -O Invoke optimizer Basic UNIX Commands
cc command – II • -o out Name the final output file out. • -Dname Define the name to the C macro processor • -Idir Seek dir for include files • Examples • cc p1.c Basic UNIX Commands
make command • Syntax • make [-f makefile] [-eiknpqrsStuwdDPBNMOg] [names] • Frequently Used Options • -f makefileDescription file is makefile • -n Print commands, but do not execute them. • -u Build all targets regardless of whether they are up-to-date or not. • Examples • make • make –f Project1.mak Basic UNIX Commands
Handling Processes • ps : Prints information about active processes • kill : Sends a signal to a process • ipcs : Reports IPC facilities status • ipcrm : Removes IPC resource id Basic UNIX Commands
ps command • Syntax • ps [-Options] • Description • Prints information about active processes. • Frequently Used Options • -A Every process now running • -e Same as -A • -f Full listing • -l Long listing • Examples • ps -ef Basic UNIX Commands
kill command • Syntax • kill [-signal] pid . . . • kill –l (the letter ‘L’ in lowercase) • Description • Sends a signal to the specified processes. • The value of signal may be numeric or symbolic. • Signal 15 is the default signal. • kill –l lists the defined signals. • Examples • kill 389 • kill –3 401 402 • kill -HUP 99999 Basic UNIX Commands
ipcs command • Syntax • ipcs [-Options] • Description • Prints information about active IPC facilities. • Without options, information is printed for message queues, shared memory, and semaphores that are currently active in the system. • Frequently Used Options • -q Message queues • -m Shared memory segments • -s Semaphores • Examples • ipcs -q Basic UNIX Commands
ipcrm command • Syntax • ipcrm [-Options] • Description • Removes messages, semaphore or shared memory identifiers. • Frequently Used Options • -q msqidRemoves the message queue id • -m shmidRemoves the shared memory segment id • -s semidRemoves the semaphore id • Examples • ipcrm -q 231 Basic UNIX Commands
Archiving and Compressing • tar : Tape archiver • compress, uncompress, zcat : Compresses and expands data using adaptive Lempel-Ziv coding • gzip : Compresses data using Lempel-Ziv coding • gunzip, gzcat : Decompresses files created by gzip, zip, compress, or pack • pack, unpack, pcat : Compresses and expands files using Huffman codes Basic UNIX Commands
tar command - I • Syntax • tar key [arguments] [name...] • Description • Saves and restores multiple files on a single file. • The key argument controls tar's actions. • Frequently Used Functions • c Create • x Extract from the tape • t List files on the tape Basic UNIX Commands
tar command - II • Frequently Used Modifiers • v Verbose • f Next argument is the name of the archive • Examples • tar cvf my.tar ./mydir1 ./mydir2 • tar tvf my.tar • tar xvf my.tar Basic UNIX Commands
compress command • Syntax • compress [ -f ] [ -v ] [ -c ] [ -V ] [ -d ] [ -b bits ] [ name ... ] • Description • Compresses and expands data • Compressed file name is *.Z • Frequently Used Options • -c Write output on standard output • -d Uncompress • -v Verbose • Examples • compress my.tar • compress -d my.tar.Z Basic UNIX Commands
uncompress command • Syntax • uncompress [ -f ] [ -v ] [ -c ] [ -V ] [ name ... ] • Description • Uncompresses files • Same as compress –d • Frequently Used Options • -c Write output on standard output • -v Verbose • Examples • uncompress my.tar.Z Basic UNIX Commands
zcat command • Syntax • zcat [ name . . . ] • Description • Uncompresses files • Same as uncompress –c • Writes the uncompressed data on standard output • Examples • zcat my.tar.Z > my.tar Basic UNIX Commands
gzip command • Syntax • gzip [ -acdfhlLnNrtvV19 ] [-S suffix] [ name . . . ] • Description • Compresses and expands data • Suffix.gz • Frequently Used Options • -c Write output on standard output • -d Uncompress • -h Help • -r Recursive • -v Verbose Basic UNIX Commands
gunzip command • Syntax • gunzip [ -acfhlLnNrtvV ] [-S suffix] [ name ... ] • Description • Uncompresses files (Same as gzip –d ) • Automatically detects input format • Frequently Used Options • -c Write output on standard output • -h Help • -r Recursive • -v Verbose Basic UNIX Commands
gzcat command • Syntax • gzcat [ -fhLV ] [ name . . . ] • Description • Uncompresses files (Same as gunzip –c) • Writes the uncompressed data on standard output • Examples • gzcat myfile.gz > myfile Basic UNIX Commands
pack command • Syntax • pack [ - ] [ -f ] name . . . • Description • Compresses files • Suffix.z • Directories cannot be compressed • Options • -f Force packing • Examples • pack myfile Basic UNIX Commands
unpack command • Syntax • unpack name . . . • Description • Expands files created by pack • Each .z files is replaced by its expanded version • The new file has the .z suffix stripped from its name • Examples • unpack myfile.z Basic UNIX Commands
pcat command • Syntax • pcat name . . . • Description • Uncompresses files created by pack • Files are unpacked and written to the standard output • Examples • pcat myfile.z • pcat myfile • pcat myfile.z > myfile Basic UNIX Commands
Other Useful Commands • grep : search files for a pattern • man : on-line reference manuals • wc : word, line and byte or character count Basic UNIX Commands
grep command - I • Syntax • grep [-E| -F] [-c| -l| -q] [-insvx] pattern_list [file . . .] • Description • Searches the input files, selecting lines matching one or more patterns • Frequently Used Options • -i Case-insensitive search • -l Write file names only • -n Display line number Basic UNIX Commands
grep command - II • Examples • grep -i unix p1.c • grep -n UNIX *.c *.h • ps –ef | grep mary Basic UNIX Commands
man command • Syntax • man [-Options] [-M path] [-T macropackage] [ -s section] name ... • man [-M path] -k keyword ... • Description • On-line reference manuals • Frequently Used Sections • 1 User commands and application programs • 2 System calls • 3 Library functions • Examples • man -s 1 mkdir • man mkdir • man -k pipe Basic UNIX Commands
wc command • Syntax • wc [ -c|-m ] [ -lw ] [ file . . . ] • Description • Counts lines, words, and characters • Options • -c Count the number of bytes • -m Count the number of characters • -l Count the number of newline characters • -w Count the number of words • Examples • wc -l *.h *.c Basic UNIX Commands