Reaction Mechanisms
270 likes | 511 Vues
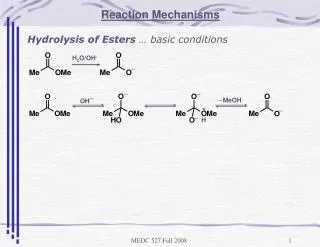
_. _. _. _. MeOH. OH. _. +. _. H. Reaction Mechanisms. Hydrolysis of Esters … basic conditions. H 2 O/OH -. _. Reaction Mechanisms. Basic Hydrolysis of Esters. electronic and steric effects …… pG-Ph-COOEt …… CH 3 COOR. Order of Reactivity G = -NO 2 -Cl -H -CH 3

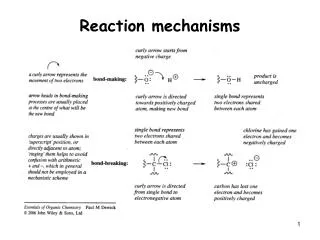
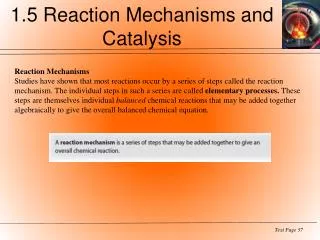
Reaction Mechanisms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
_ _ _ _ MeOH OH _ + _ H Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of Esters … basic conditions H2O/OH- _ MEDC 527 Fall 2008
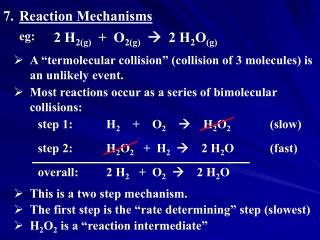
Reaction Mechanisms Basic Hydrolysis of Esters electronic and steric effects …… pG-Ph-COOEt …… CH3COOR Order of Reactivity G = -NO2 -Cl -H -CH3 -OMe Order of Reactivity R = -Me -Et -i-Pr -t-Bu MEDC 527 Fall 2008
H2O/H+ + MeOH + + + H H + _ H2O H MeOH + H + Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of Esters … acidic conditions MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Acidic Hydrolysis of Esters electronic and steric effects …… pG-Ph-COOEt …… CH3COOR (G = NO2 < Cl < H < CH3 < OMe) (R = Me > Et > I-Pr > t-Bu) Order of Reactivity G = -NO2 -Cl -H -CH3 -OMe Order of Reactivity R = -Me -Et -i-Pr -t-Bu MEDC 527 Fall 2008
H2O/OH- _ NH4+ _ _ _ _ + OH NH3 NH4 + _ _ Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of Amides … basic conditions MEDC 527 Fall 2008
_ _ + + _ H H H2O NH3 H + NH4 _ + + + Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of Amides … acidic conditions H2O/H+ _ NH4+ MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of other carboxylic acid derivatives lactone lactam anhydride imide carbonate carbamate urea MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of drugs Ritonavir (HIV protease inhibitor) MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Hydrolysis of drugs Neocarzinostatin A (anti-tumor) MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Predict ‘metabolites’ Propanidid (anesthetic) {Ester > 3O Amide electronic + steric effect} MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Predict ‘metabolites’ Cocaine MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Reaction Mechanisms Predict ‘metabolites’ > > Pilocarpine Isopilocarpine Hydrolysis of pilocarpine is much faster than that of isopilocarpine {Stereochemical effect} MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Aromatic Structures ….. Examples MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Definition of EAS and Examples MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Mechanism + + + NO2+ + + MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Substituent Effects Types of Substituent Effects • Activating/Deactivating groups • Directors - o, p, and m MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Substituent Effects • Activating: o-, p- directors • Strongly activating • -NH2, -NHR, -NR2 • -OH • Moderately activating • -OR • -NHCOCH3 • Weakly activating • -Ph • -R • Deactivating: m-directors • -NO2, -N(CH3)3+, -CN, -COOH, -COOR, -SO3H, -CHO, -COR • Deactivating: o-,p- directors • -F, -Cl, -Br, -I MEDC 527 Fall 2008
+ + + Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Theory of Reactivity ArH + Y+ ArY + H+ , where Y = -COCH3, or –NO2, or –Cl, etc. MEDC 527 Fall 2008
+ + + + + + + + + Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Theory of Orientation o-, p- directors m- directors eD groups eW groups MEDC 527 Fall 2008
_ _ _ + Ortho attack + + + + + Meta attack _ _ _ + Para attack + + + _ _ _ + Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Theory of Orientation … the anomalous effect of halogens Note: Y is the incoming electrophile MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Net Effect of Substituents in Directing the Incoming Group MEDC 527 Fall 2008
1 % 62% 37% Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Net Effect of Substituents in Directing the Incoming Group MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Relevance of EAS to Drugs MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Relevance of EAS to Drugs MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Relevance of EAS to Drugs MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Relevance of EAS to Drugs MEDC 527 Fall 2008
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Relevance of EAS to Drugs MEDC 527 Fall 2008