System of Linear Equations
80 likes | 298 Vues
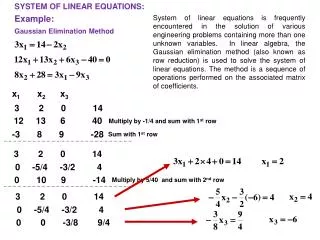
Solving the Linear Equation by Using the Gauss Elimination & the Back-Substitution. Soongsin Joo. System of Linear Equations. Method of Gauss Elimination & Back-Substitution. A: n n matrix , x and b: n-vector. Gauss Elimination. Gauss Elimination. .

System of Linear Equations
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Solving the Linear Equation by Using the Gauss Elimination & the Back-Substitution Soongsin Joo • System of Linear Equations • Method of Gauss Elimination • & Back-Substitution
A: nn matrix , x and b: n-vector Gauss Elimination Gauss Elimination : Upper-Triangular Matrix
(Gauss Elimination) Initialize the n-vector p to have pi = i (i=0,,n-1). For j = 0,∙∙∙,n-2, do; Find (the smallest) k≥j such that . If (w[p[k]][j]==0) A is not invertiable and stop. else pk pj (Exchange the contents) For k = j, ∙∙∙,n-1, do; set and r equal to . For i = j,∙∙∙, n, do; set . If (w[p[k]][j]==0), A is not invertiable and stop. Algorithm
[Input the Upper-triangular Matrix W] Define matrix W in the system Ax = b. Work-Matrix: W=(A b), W: n(n+1) (Back substitution) For k = n-2, n-3,∙∙∙,0 , do; calculate . Algorithm
Sloving the Linear Equation (1/3) /* Solving the Linear Equation by Using the Gauss Elimination & the Back-Substitution */ /* Include Header Files */ #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> #include <conio.h> /* Define Global variable */ int i,j,k,l; int n; int p[3]; /* Pivot Vector */ /* Working Matrix */ float w[3][4] = {{2,3,-1,5},{4,4,-3,3},{-2,3,-1,1}}; float A[3][3],b[3],x[3]; char FOUTN[20]; FILE *FOUT; /* System of the Linear Equations */ /*Gauss function is calculated for the upper-triangular working matrix*/ void Gauss(); /*Bsub function is calculated for the solution vecter x*/ void Bsub(); /* Main Routine */ void main(){ n=3;/* No. of Rows in W */ /*Input the Name of the Output File and Open It */ printf("\nINPUT THE NAME OF THE OUTPUT FILE\n"); scanf("%s",FOUTN); if((FOUT=fopen(FOUTN,"w"))==NULL){ printf("FILE OPEN ERROR...\n"); getch(); exit(-1); } /* Print Initial Matrix W */ printf("\n Initial Matrix \n"); fprintf(FOUT,"\n Initial Matrix \n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++){ for(j=0;j<n+1;j++){ printf("%10.2f",w[i][j]); fprintf(FOUT,"%10.2f",w[i][j]); } printf("\n"); fprintf(FOUT,"\n"); }
Sloving the Linear Equation (2/3) Gauss(); /*Working matrix W is divided into A[][] and b[]*/ for(i=0;i<n;i++){ for(j=0;j<n;j++){ A[i][j]=w[p[i]][j]; } } for(k=0;k<n;k++){ b[k]=w[p[k]][n]; } Bsub(); /* Print the Output */ printf("\n Result of Gauss Elimination \n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++){ for(j=0;j<n+1;j++){ printf("%10.2f",w[p[i]][j]); } printf("\n"); } printf("\n - Solution -\n"); for(j=0;j<n;j++){ printf(" x%d =%5.2f\n",j+1,x[j]); } printf("\n\n******* END *******\n"); /* Fileout the Result */ fprintf(FOUT,"\n Result of Gauss Elimination \n"); for(i=0;i<n;i++){ for(j=0;j<n+1;j++){ fprintf(FOUT,"%10.2f",w[p[i]][j]); } fprintf(FOUT,"\n"); } fprintf(FOUT,"\n - Solution -\n"); for(j=0;j<n;j++){ fprintf(FOUT," x%d =%5.2f\n",j+1,x[j]); } fprintf(FOUT,"\n\n******* END *******\n"); fclose(FOUT); getch(); } void Gauss(){ float r,s; /* Initialize the Pivot vector */ for(i=0;i<n;i++){ p[i]=i; }
Sloving the Linear Equation (3/3) for(j=0;j<n-1;j++){ for(k=j;k<n+1;k++){ if(k==n){ printf(" W is not invertible!!"); getch(); exit(-1); } else if(w[p[k]][j]==0)continue; else{ for(l=j+1;l<n+1;l++){ s=w[p[k]][l]; /* Exchange the contents of p[k] and p[j] */ w[p[k]][l]=w[p[j]][l]; w[p[j]][l]=s; } break; } } /* for i=j+1,.........,n-1 do; set r=w[p[i]][j]/w[p[j]][j] */ for(i=k+1;i<n;i++){ r=w[p[i]][j]/w[p[j]][j]; /* For k=j,........,n do; set w[p[i]][k] = w[p[i]][k]-r*w[p[j]][k] */ /* starting value of j is j+1. the source elements are not counted zero. Thus, starting value of k is j as it calculated to give all the elements. */ for(k=j;k<n+1;k++){ w[p[i]][k] = w[p[i]][k] - r*w[p[j]][k]; } } } } void Bsub(){ int t; x[n-1]=b[n-1]/A[n-1][n-1]; for(k=n-2;k>=0;k--){ t=0; for(j=k+1;j<n;j++){ t+=A[k][j]*x[j]; x[k]=(b[k]-t)/A[k][k]; } } }