Advanced Driving Control Architecture for Intelligent Systems
60 likes | 188 Vues
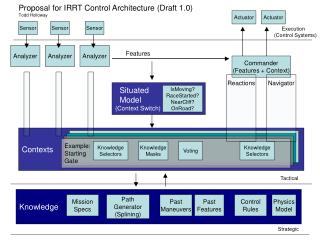
This document outlines a comprehensive control architecture for driving systems that integrates various components such as sensors, analyzers, and actuators. It emphasizes the importance of identifying context switches and updating situated models in real-time for effective maneuvering. The architecture includes features for tactical and strategic responses, knowledge selectors, and a path generator using spline-based methods. The proposal covers the integration of past maneuvers, control rules, and mission specifications to enhance decision-making, ensuring fluid adaptation in complex environments.

Advanced Driving Control Architecture for Intelligent Systems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Actuator Actuator Sensor Sensor Sensor Analyzer Analyzer Analyzer Commander (Features + Context) Reactions Navigator Situated Model (Context Switch) IsMoving? RaceStarted? NearCliff? OnRoad? Contexts Example: Starting Gate Knowledge Selectors Knowledge Masks Voting Knowledge Selectors Knowledge Mission Specs Path Generator (Splining) Past Maneuvers Past Features Control Rules Physics Model Proposal for IRRT Control Architecture (Draft 1.0) Todd Holloway Execution (Control Systems) Features Tactical Strategic
Contexts Example: Starting Gate Knowledge Selectors Knowledge Masks Voting Knowledge Selectors Contexts • Interface between system components and system knowledge • Starting Area, Lake Bed, Climbing Hill, Cliff-side Road, Water, Failure Modes, etc. • Multiple contexts simultaneously (?)
Situated Model (Context Switch) IsMoving? RaceStarted? NearCliff? OnRoad? Model • Only purpose is to identify when context(s) need to be changed • Needs to be continually updated • Simplistic, does need to include all features that may come from sensors • Hard-coded vs. Learned
Knowledge Mission Specs Path Generator (Splining) Past Maneuvers Past Features Control Rules Physics Model System Knowledge • Mission specification: Start, Goals, Waypoints, Corridors • Path Generator (Splining Model) • Case Bases: Past features detected, actions, routes to aid and speed up decision making as well as fill in gaps in driving model • Hand coded (or learned) control rules and case adaptation rules • A driving (physics) model specifying action/change
Sensor Sensor Sensor Analyzer Analyzer Analyzer Analyzers • Feature detection, object recognition, etc. • May use knowledge, as accessible in the current context, to aid these tasks
Actuator Actuator Commander (Features + Context) Reactor Navigator Commander • Purpose is to select actions that should be performed • Handles voting (within the current context) among input features and between reacting immediately or consulting the navigator. • Decides how long (within the current context) before issuing the next actions to perform. That is, it decides when to cut off the navigator as it devises a solution.