Understanding Daily Nutrition Values and Healthy Weight Management
110 likes | 224 Vues
This guide outlines essential nutrition values based on a 2,000-calorie diet, including recommended servings for grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy, and proteins. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining weight by balancing calorie intake with energy expenditure, detailing how consuming more or fewer calories affects body weight. The document also discusses pre-game meal strategies for athletes, the Body Mass Index (BMI), Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR), and the Harris-Benedict Equation for calorie calculation. Additionally, it touches on the Female Athlete Triad and eating disorders such as anorexia and bulimia, highlighting their implications for health.

Understanding Daily Nutrition Values and Healthy Weight Management
E N D
Presentation Transcript
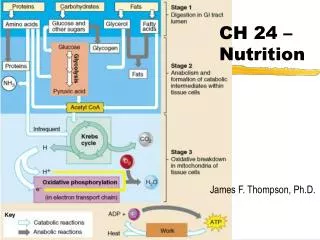
Ch. 8 Nutrition Part 2
Daily Value • Found on all food labels • Based on a 2,000 calorie diet • Guidelines • Fat: 30% of calories • Carbohydrates: 60% of calories • Protein: 10% of calories
Recommended Servings • Grains: about 6 ounces, at least half should be whole grain • Vegetables: 2.5-3 cups • Fruit: 2 cups • Dairy: 3 cups • Protein: 5.5-6.5 oz • Oils: 6-7 teaspoons
Maintaining Weight • If you consume the same number of calories as your body requires, you will maintain the same weight • If you consume more than your body needs, you will gain weight • If you consume less than your body needs, you will lose weight
Maintaining Weight • One pound of fat is approximately 3,500 calories • Losing Weight • Diet • Exercise • Gaining Weight • Increase calorie intake but must make sure it is not high in fat
Pre-Game Meals • Consumed 3-4 hours before the game • High carbohydrates and fluids • Moderate intake of proteins • Avoid caffeine • Small snack such as peanut butter crackers, bananas, water approx. 1-2 hours before
BMIand BMR • Body Mass Index (BMI) • BMI=Wt. in lbs ÷ Ht. in in.÷ Ht. in in. × 703 • Normal = 18.5-24.9 • Overweight = 25-29.9 • Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) • Women: BMR = 655 + ( 4.35 x weight in pounds ) + ( 4.7 x height in inches ) - ( 4.7 x age in years ) • Men: BMR = 66 + ( 6.23 x weight in pounds ) + (12.7 x height in inches ) - ( 6.8 x age in year )
Harris Benedict Equation • If you are sedentary (little or no exercise) : Calorie-Calculation = BMR x 1.2 • If you are lightly active (light exercise/sports 1-3 days/week) : Calorie-Calculation = BMR x 1.375 • If you are moderately active (moderate exercise/sports 3-5 days/week) : Calorie-Calculation = BMR x 1.55 • If you are very active (hard exercise/sports 6-7 days a week) : Calorie-Calculation = BMR x 1.725 • If you are extra active (very hard exercise/sports & physical job or 2x training) : Calorie-Calculation = BMR x 1.9
Female Athlete Triad • Disordered eating • Amenorrhea-absence of menstrual cycle • Osteoporosis-bone loss • Most common in sports that emphasize leanness
Anorexia Nervosa • Psychophysiological disorder where the person has an abnormal fear of being obese • Most commonly in young women • Substantial weight loss • Fatigue and dizziness • Osteoporosis • Heart failure
Bulimia • Eating disorder characterized by binge eating and purging • Common in young women of normal weight • Dental cavities • Stomach ulcers • Weight fluctuations • Damage to esophagus