Faraday’s Law
290 likes | 1.78k Vues
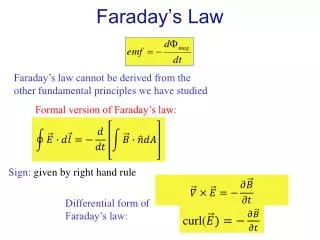
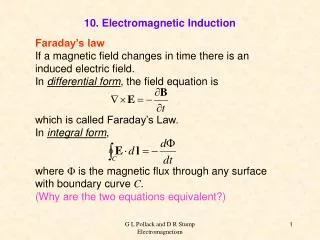
Faraday’s Law. Faraday’s law cannot be derived from the other fundamental principles we have studied. Formal version of Faraday’s law:. Sign: given by right hand rule. Differential form of Faraday’s law:. c url(. Two Ways to Produce Changing . Two ways to produce curly electric field:

Faraday’s Law
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Faraday’s Law Faraday’s law cannot be derived from the other fundamental principles we have studied Formal version of Faraday’s law: Sign: given by right hand rule Differential form of Faraday’s law: curl(
Two Ways to Produce Changing Two ways to produce curly electric field: 1. Changing B 2. Changing A
Inductance For long solenoid: R emfbat emfcoil Constant voltage – constant I, no curly electric field. Increase voltage:dB/dt is not zero emf Change current at rate dI/dt: (one loop)
Inductance ENC EC R emfbat R emfind emfbat emfcoil Increasing I increasing B L – inductance, or self-inductance
Inductance ENC EC L R emfbat emfind Unit of inductance L: Henry = Volt.second/Ampere Increasing the current causes ENC to oppose this increase
Inductance: Decrease Current ENC EC R L emfbat emfind Conclusion: Inductance resists changes in current Orientation of emfind depends on sign of dI/dt
Field Energy Density Electric and magnetic field energy density:
Current in RL Circuit If t is very long:
Current in RL Circuit Current in RL circuit: If t is zero:
Time Constant of an RL Circuit Current in RL circuit: Time constant: time in which exponential factor become 1/e
Current in an LC Circuit Current in an LC circuit Period: Frequency:
Energy in an LC Circuit Initial energy stored in a capacitor: At time t= :Q=0 1/4 of a period At time t=0:Q=Q0 System oscillates: energy is passed back and forth between electric and magnetic fields.
Energy in an LC Circuit At time t= : What is maximum current? At time t=0:
LC Circuit and Resonance Radio receiver: Frequency:
Two Bulbs Near a Solenoid Varying B is created by AC current in a solenoid What is the current in this circuit? Advantage of using AC:Currents and emf ‘s behave as sine and cosine waves.
Two Bulbs Near a Solenoid Add a thick wire: I1 Loop 1 I2 Loop 2 I3 Loop 1: Loop 2: Node:
Two Bulbs Near a Solenoid Add a thick wire: I1 Loop 1 I2 Loop 2 I3 Loop 1: Loop 2: Node: