MASTOIDITIS
600 likes | 5.88k Vues
NURSING CARE OF. MASTOIDITIS. Ni Ketut Alit A Nursing Faculty Airlangga University Surabaya East Java. REFERENCES. Black , J.M. & Matassarin E, (1997). Medical Surgical Nursing: Clinical Management for continuity of care . J.B. Lippincott.co.

MASTOIDITIS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
NURSING CARE OF MASTOIDITIS Ni Ketut Alit A Nursing Faculty Airlangga University Surabaya East Java.
REFERENCES • Black, J.M. & Matassarin E, (1997). Medical Surgical Nursing: Clinical Management for continuity of care. J.B. Lippincott.co. • Barbara C.L & Wilma J.P. (2006). Essentials of Medical Surgical Nursing. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. • Smeltzer, S.C., & Bare, B. (2003). Brunner and Suddarth's Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing (10th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. • Ignativicius & Bayne. (2001). Medical and Surgical Nursing. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company. • Luckman & Sorensen. (2000). Medical Surgical Nursing. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company. • Journals and article related to..
OVERVIEW The epithelial lining of the middle ear <continous> The epithelial lining of the mastoid air cells (Embedded in the temporal bone) Mastoiditis is a secondary disorder resulting inadequated treated Otitis Media. Mastoiditis can be either acute or chornic; it was leading cause of death in children and hearing lossmin adults
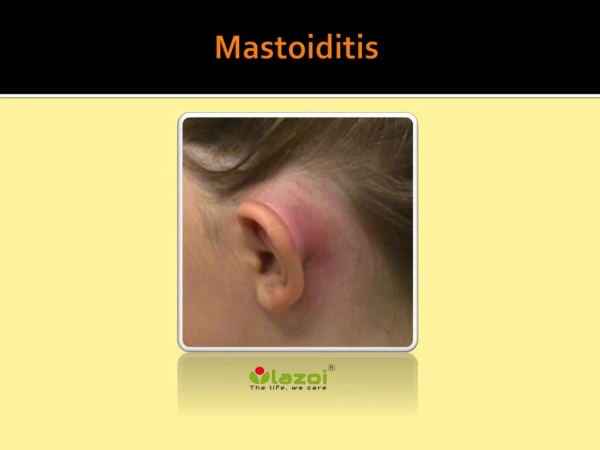
ASSESMENT: The clinical manifestations of mastoiditis include: • Swelling behind the ear • Pain with minimal movement of tragus, the pinna, or the head. • Cellulitis develops on the skin or external scalp over mastoid process • Clients withsmastoiditis also have low grade fever, malaise, and anoreksia
Otosscopic Examination Reveals : • a red, dull, thick, immobile tympanic membrane with or without perforation • Postauricuar lymph nodes are tender and enlarge.
TREATMENT Non Surgical management: Antibotic therapy is aimed at preventing the continued spread of infection from the otitis media or mastoiditis. But it has limited use in the actual treatment of mastoiditis because of the difficulty of acchieving effective antibiotic levels within the bony structure of mastoid. Culture material is obtained from the ear drainage or by myringotomy.
Surgical Management • Surgical removal of the infected tissue is necessary if the client does not respond to antibiotic administrationwithin a few day. • A simple or modified radical mastoidectomy with tympanoplasty is the most common treatment. • All infected tissue must be removed so that the infection doesnot spread to other structures.
NURSING ROLE IN PERIOPERATIVE CARE • Reassures the client that operative will relive pain • Discusses the reason for the prosedure with the client and relieve anciety • Cleans the exteral canal with a bacteriostatic solution
Education Guide Recovery From Ear Surgery • Avoid straining when you have bowel elimination. • Do not drink through a straw for 2-3 wk • Avoid air travel for 2-3 wk • Stay away from people with cold • Avoid getting your head wet, washing hair,and showering for 1 wk • Keep yor ear dry for 6 wk by placing a ball cotton change daily • Avoid rapidly moving the head for 3 wk • Change eardressing every 24 hour • Report excessive drainage
COMPLICATION Compication arise : • Infective material has not been removed completely. • Contamination of other structure outside the mastoid and middle ear. Complication include : Damage to the abducens (NC VI) and facial cranial nerves (NC VII) • Decreasing ability to look laterally • Dropoping the mouth on the affected side
Other Complication • Vertigo • Meningitis • Brain abcess • Chronic purulent otitis media • Wound infection
PHISICAL ASSESMENT • Early manifestation of mastoiditis development PSYCHOSOCIAL ASSESMENT Fear of losing hearing Deny that the change occurred
NURSING PROBLEM • Pain • Sensory /perceptual alteration (auditory) • Risk of infection • Hipertermi • Anciety
QUESTION… • Write down education guide for client post surgery with mastoiditis!!