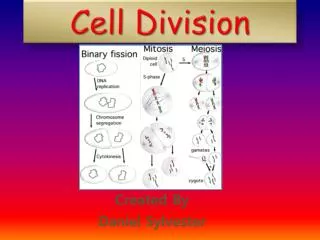
CELL DIVISION
420 likes | 659 Vues
By Jakey Wakey Artaflakey . CELL DIVISION . 3 steps of Interphase G 1 - cell growth which makes the cell get bigger. ?. ?. Interphase. 3 steps of Interphase G 1 - cell growth which makes the cell get bigger. ?. ?. Interphase. Centrioles. 3 steps of Interphase

CELL DIVISION
E N D
Presentation Transcript
By Jakey Wakey Artaflakey CELL DIVISION
3 steps of Interphase • G1- cell growth which makes the cell get bigger. ? ? Interphase
3 steps of Interphase • G1- cell growth which makes the cell get bigger. ? ? Interphase
Centrioles • 3 steps of Interphase • G1- cell growth which makes the cell get bigger. • S- DNA replication which the DNA copies itself. • G2- Centrioles duplicates. ? ? Interphase DNA Nucleus Nucleolus Nuclear envelope
This is the longest of all the phases. • Chromatin come together to form tight Chromosomes. • Nucleolus and nuclear envelope disappear. ? ? Prophase Chromatin
This is the shortest of all the phases. • Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell. • Spindle attaches to each chromosome. ? ? Metaphase
This is the shortest of all the phases. • Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell • Spindle attaches to each chromosome. ? ? Metaphase
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Chromosomes are pulled apart. • Chromatids now become individual chromosomes. ? ? Anaphase Sister chromatids
Nuclear envelope reforms. • Nucleolus reappears. ? ? Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms. • Nucleolus reappears. ? ? Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms. • Nucleolus reappears. ? ? Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms. • Nucleolus reappears. ? ? Telophase
Nuclear envelope reforms. • Nucleolus reappears. • DNA unwinds to form chromatin again. • Spindle breaks apart. ? Spindle fibers ? Telophase
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
The cell fully pinches in forming a cleavage furrow. • In the end there are two cells that have the exact same DNA. ? Spindle fibers ? Cytokinesis
Then it repeats that cycle forever. Cell Division
3 steps of Interphase • G1- cell growth which makes the cell get bigger. • S- DNA replication which the DNA copies itself. • G2- Centrioles duplicates. ? ? Interphase