Geometry and Measurement
190 likes | 425 Vues
Geometry and Measurement. 9/8/06. van Hiele Levels. Sequential Not age dependent like Piaget Geometric experience = advancement Instruction and language should be developmentally appropriate Learn algorithms without knowing the concept. Level 0: Visualization. Sorting and classifying

Geometry and Measurement
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Geometry and Measurement 9/8/06
van Hiele Levels • Sequential • Not age dependent like Piaget • Geometric experience = advancement • Instruction and language should be developmentally appropriate • Learn algorithms without knowing the concept
Level 0: Visualization • Sorting and classifying • Triangles vs non-triangles • Shapes with all straight sides vs others • Transformations • Tangrams • Soma cube puzzles • Pattern block puzzles
Level 0: Visualization • Constructions with… • Geoboards • Tessellations with pattern blocks • Pentominoes • Shape Hunts • Go find as many different two-dimensional shapes • Location bingo
Level 1: Analysis • Sorting by characteristics of 2-D or 3-D shapes • Right triangles vs non-right triangles • Quadrilateral sort Squares Rhombus Rectangles Trapezoids Quadrilaterals Kites Parallelogram What similarities do you notice???
Level 1: Analysis • Sorting by characteristics of 2-D or 3-D shapes • Right triangles vs non-right triangles • Quadrilateral sort 4-sided polygon Quadrilaterals Quad with at least one pair of parallel sides Trapezoids Kites Quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides Parallelogram Quad with two pairs of parallel sides Rectangles Parallelogram with 4 right angles Other Quadrilaterals Parallelogram with 4 congruent sides Rhombus Quadrilaterals that don’t fit elsewhere Parallelogram with 4 right angles and 4 congruent sides Squares
Level 1: Analysis • Sorting by characteristics of 3-D shapes • Faces, vertices, edges Shapes with 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges Shapes with a circular base
Level 1: Analysis • Area and perimeter with manipulatives • Use square tiles to determine the area and perimeter of a piece of paper Algorithms for these are appropriate for level two!!
Level 2: Informal Deduction • MDL’s- “minimal defining lists” • Minimal: if anything is removed the definition is incorrect • Defining- any object with this definition must be that shape • a square= quadrilateral with 4 right angles and 4 congruent sides 1 2 3 triangle with one right angle a right triangle = 1 2
Level 2: Informal Deduction • Shape decomposition • Start with an isosceles triangle • Make two shapes that have 7 sides • Make three shapes that have 11 sides • Start with a regular hexagon • Make two shapes that have 8 sides • Make two shapes that have 9 sides • Start with a square • Make three triangles- two of the three need to be congruent
Level 2: Informal Deduction • Spatial visualization • Using wooden blocks build the following figure: Left Top Back Front Right
Level 2: Informal Deduction • Nets of a cube • Using square tiles place six tiles together so that all share at least a side with another square. • How many different arrangements can you make?
Level 2: Informal Deduction • There are 11 nets of a cube.
Level 2: Informal Deduction Always, sometimes or never??? • Triangles have one right angle. • Squares are rectangles. • Quadrilaterals are rectangles. • Parallelograms have a right angle. • Prisms all have six faces.
vanHielle Levels and Cognitively-appropriate Manipulative Levels
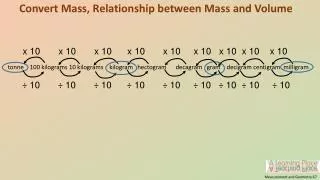
Measurement- Length • Concrete • Using non-standard units to measure length • How long is the book (in pencils)? • Using rulers to measure length • Representational • Paper representations with a scale • Symbolic • Conversions • 18 inches = __ feet • 5 inches = ___ cm
Measurement- Area/Perimeter • Concrete • Measuring with non-standard units (e.g., tiles) • Measuring with rulers • Representational • What is the area of the square? • Symbolic • Using area and perimeter formulas
Measurement- Volume • Concrete • Using cylinders to measure volume • Objects- beans • Liquid (e.g., water) • Representational • What is the volume of the figure? • Symbolic • Using formulas for volume • Volume = Base area * height (for prisms, cylinders)