10.3 Polygenic Inheritance
80 likes | 515 Vues
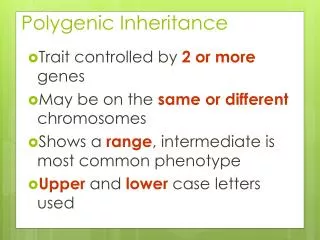
10.3 Polygenic Inheritance. HL Material. Polygenic Inheritance. Concerns a single characteristic that is controlled by more than one gene Each allele only contributes a small amount to the overall phenotype of the individual The more genes involved, the more variation

10.3 Polygenic Inheritance
E N D
Presentation Transcript
10.3 Polygenic Inheritance HL Material
Polygenic Inheritance • Concerns a single characteristic that is controlled by more than one gene • Each allele only contributes a small amount to the overall phenotype of the individual • The more genes involved, the more variation • examples: human skin colour, height, shape of comb in poultry
Polygenic Inheritance • Contributes to continuous variation rather than an either “on” or “off” version of the trait a) Is the genotypic variation in the population. The more genes involved with the characteristic the greater the number of phenotypic classes. (b) Phenotypic variation = genotypic variation + environmental variation. The environmental component smoothes the genotypic category differences.
Example: Skin Colour • Controlled by as many as 4 genes • Alleles control the production of malanin (pigment that colours skin) • Example: two genes involved; two individuals heterozygous at both alleles • A: melanin (value of 1) • a: no melanin (value of 0) • B: melanin (value of 1) • b: no melanin (value of 0)
Parental Genotypes: AaBb x AaBb • Parental Gametes: • Set up a dihybrid cross
What happens if there are 3 genes involved? • Parental Genotype: AaBbCc x AaBbCc