An Introduction to Forces: More Practice
250 likes | 526 Vues
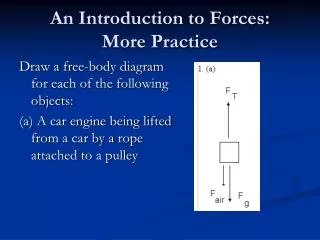
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice. Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following objects: (a) A car engine being lifted from a car by a rope attached to a pulley. An Introduction to Forces: More Practice. Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following objects:

An Introduction to Forces: More Practice
E N D
Presentation Transcript
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following objects: (a) A car engine being lifted from a car by a rope attached to a pulley
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following objects: (b) an car moving with constant velocity on a level road
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following objects: (c) an apple hanging from a tree branch
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Draw a free-body diagram for each of the following objects: (d) a skydiver being slowed by a parachute
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Ms. Rosebery is pulling across level snow a sled on which is sitting her daughter Ivy. Tied to the back of Ivy's sled is another tiny sled on which Ivy's baby doll is sitting. Draw the free-body diagrams for (a) Ms. Rosebery
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Ms. Rosebery is pulling across level snow a sled on which is sitting her daughter Ivy. Tied to the back of Ivy's sled is another tiny sled on which Ivy's baby doll is sitting. Draw the free-body diagrams for (b) Ivy
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Ms. Rosebery is pulling across level snow a sled on which is sitting her daughter Ivy. Tied to the back of Ivy's sled is another tiny sled on which Ivy's baby doll is sitting. Draw the free-body diagrams for (d) Ivy’s sled
An Introduction to Forces: More Practice Ms. Rosebery is pulling across level snow a sled on which is sitting her daughter Ivy. Tied to the back of Ivy's sled is another tiny sled on which Ivy's baby doll is sitting. Draw the free-body diagrams for (d) Ivy’s doll’s sled
Newton’s 1st Law of Motion: Learning Goal The student will be able to state Newton’s 1st Law and apply it in qualitative and quantitative terms to explain the effect of forces acting on objects. (B3.4)
Net Force The net force is the sum of all forces acting on an object. Example: A weightlifter holds a weight above his head by exerting a force of 1.6 kN [up]. The force of gravity acting on the weight is 1.6 kN [down]. Draw a FBD of the weight. What is the net force on the weight?
Net Force FA=1.6 kN Fg=1.6 kN
Net Force The net force is zero: 1.6 kN + (-1.6 kN) = 0 FA=1.6 kN Fg=1.6 kN
Newton’s First Law of Motion If there is no net force acting on an object, the object will remain at rest
Newton’s First Law of Motion If there is no net force acting on an object, the object will remain at rest
Newton’s First Law of Motion If there is no net force acting on an object, the object will remain at rest or will keep moving at the same constant velocity.
Newton’s First Law of Motion If there is no net force acting on an object, the object will remain at rest or will keep moving at the same constant velocity. (Conversely, if an object is at rest or is moving at constant velocity, there is no net force acting upon it.)
Inertia This is the principle of inertia, first articulated by Galileo:
Inertia Inertia is the property of matter that causes it to resist changes to its motion. The greater the mass of an object, the greater its inertia. “Inertia is a property of matter.”
Newton’s First Law of Motion Question: An object is being pushed along at constant velocity by a force of 5 N [left]. What is the force of friction acting on the object?
Newton’s First Law of Motion Question: An object is being pushed along at constant velocity by a force of 5 N [left]. What is the force of friction acting on the object? If the velocity is constant, there is no net force, so the force of friction must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the applied force:
Newton’s First Law of Motion Question: An object is being pushed along at constant velocity by a force of 5 N [left]. What is the force of friction acting on the object? If the velocity is constant, there is no net force, so the force of friction must be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the applied force: Ff = 5 N [right]
More Practice Explaining Why with Newton’s 1st Law of Motion