Photosynthesis Questions
720 likes | 835 Vues
Explore the intricate processes of photosynthesis, including the roles of palisade parenchyma, guard cells, and stomates. Learn about the pigments in photosystems, photolysis in Photosystem II, and the functions of proteins like plastoquinone and plastocyanin. Discover the significance of the Calvin cycle and the C3 and C4 pathways adapted to various climates, as well as the science behind absorption spectrums and TLC. Unravel essential concepts like Rf values and the implications of experimental results in plant physiology and respiration.

Photosynthesis Questions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
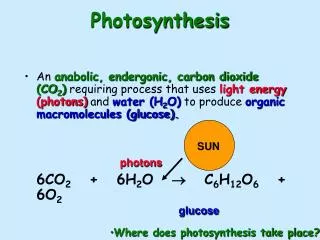
The type of tightly packed plant cells that are able to photosynthesize.
Guard cells form an opening in the lower epidermis called what?
Yes, it contains molecules of various pigments such as, carotenoids, chlorophyl a and b.
H+ ions are pumped into the thylacoid and they diffuse out through ATP Synthase to form ATP.
Proteins in the thylacoid membrane that transfer the electrons.
What do plants do when there is not enough NADP molecules to accept electron?
They perform Cyclic photophosphorylation where the electrons excited at p700 (photosystem I) return to p700 after transferring from several membrane proteins.
When PGA is converted to G3P which goes on to form organic molecules and more RuBP, it is the ________pathway?
The pathway where plants first incorporate CO2 with PEP to form oxaloacetate and the glucose. Why do plants use this pathway?
C4 Pathway (Hot, dry climates Take advantage of intense sunlight Ex. Sugar cane and corn)
A graph showing wavelength vs absorbance of a particular substance. From the data it can be determined what specific wavelength is absorbed.
What is a “blank” needed to obtain accurate readings with a spectrophotometer?
A Blank has all of the buffer, dilutants, and or solvents used in a sample and not what is being tested.
The reference front or the distance the pigment migrated divided by the distance the solvent front moved.
Why was a flask of water places between the samples and the lamp in the lab?
To act as a heat sink….so heat would not have an effect on the results.
According to the lab, what would it indicate if the O.D. of a tube was .67 at time “O” and .65 at time “5”
It would indicate that no photosynthesis occurred in the sample.
2 Pyruvic acid molecules (pyruvate)
Glycolysis Kreb’s cycle Electron Transport Chain (Oxidative phosphorylation)
Yes, glycolysis does not require oxygen. This occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.