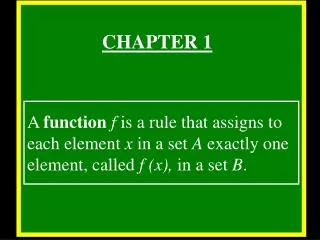
Chapter 1
400 likes | 1.25k Vues
Chapter 1. The Global Agri-Food System. The Agri-Food System. Feeding a Hungry World. Agribusiness. The Business of Food. Agri-Food. #1. In the World. U.S. Agribusiness Leading the World. Largest Agribusiness Sector in the World Largest Part of U.S. Economy

Chapter 1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 1 The GlobalAgri-Food System
The Agri-Food System Feeding a Hungry World
Agribusiness The Business of Food
Agri-Food #1 In the World
U.S. AgribusinessLeading the World • Largest Agribusiness Sector in the World • Largest Part of U.S. Economy • One of the Best Integrators of Technology • Biggest User of Biotechnology • Safest Food • Lowest Cost Food • Largest Assortment of Food • 11,000+ New Food Products per Year
Food Products Farms and Ranches FoodConsumers Product Flowin the GlobalAgri-Food System Food Retailers FoodManufacturers CommodityProcessors Food Distributors Ag Commodities What Consumers Want Input Suppliers
The Business of Food • We consume 350 million tons of food each year – about 6 pounds per person per day • Farmers get 20 cents of each food dollar • Consumers spend 10.4% disposable income on food ~ 6.2% for food at home ~ 4.2% for food away from home • Each farm worker produces enough food for 103 people – 75 in U.S. and 28 abroad • Number of farm workers is greater than the combined total of workers in the auto, steel, and transportation industries
U.S. Agribusiness With less than 7% of the world’s land and 5% of the world’s population We Produce 12% of World Agricultural Output • 47% of the world’s soybeans • 42% of the world’s corn • 28% of the world’s cheese • 19% of the world’s milk • 16% of the world’s cotton • 12% of the world’s wheat We Export 27% of U.S. Production
People Buy Food fora Hierarchy of Reasons Status and Causes Living Well Promoting Health Convenience Tastes Good and Variety Nutritious, Safe, and Affordable
Agribusiness Management:The Integrator of the Disciplines • “Science remains in the laboratory unless there is incentive to adopt the knowledge. This is the difference between science and technology. {Agribusiness Management} is the integrator.” • Source: The Agricultural Revolution of the 20th Century, Paarlberg and Paarlberg, p. 59.
The Agricultural Revolution of the Twentieth Century – I • “If a farmer from Old Testament times could have visited an American farm in year 1900, he would have recognized—and had the skill to use—most of the tools he saw: the hoe, the plow, the harrow the rake. If he were to visit an American farm today, he might think he was on a different planet.” • Source: Paarlberg and Paarlberg, p. xiii.
The Agricultural Revolutionof the Twentieth Century – II • “The changes that occurred in American agriculture during the 20th century exceed in magnitude all the changes that occurred during the 10,000 years since human beings first converted themselves from hunters and gatherers to herdsmen and cultivators.” • Source: Paarlberg and Paarlberg, p. xiii.
The Input Sector The Processing- Manufacturing Sector The Production Sector The Agri-Food System
The Commodity Processing-Food Manufacturing Sector Transforming Commoditiesto Food Products
Agribusiness is BIG Business 112 Agribusiness Firms in the Fortune 500 9 Beverage Companies—Coca-Cola, Pepsico 19 Food Consumer Products Companies—H J Heinz, Hershey 12 Food Production Companies—Tyson Foods, Gold Kist 11 Food Service Companies—McDonalds, Starbucks 19 Food and Drug Stores—Kroger, Safeway 19 Forest and Paper Products—Weyerhaeuser, Mead 7 Textile Companies—Westpoint Stevens 5 Tobacco Companies—Philip Morris 11 Food and Grocery Wholesalers—Supervalu,Sysco
The TrendsFarming to Food Factories • Fewer but larger facilities • Fewer but better educated employees • A high tech business
Discussion Questions • List and briefly describe the six parts of the global agri-food system. • Define and describe each word in the term agri-food system. • Why was agriculture a prime market for the adoption of production-enhancing and labor-saving devices during the industrial revolution? • How have Americans’ perceptions of food changed in recent years? What does this mean for firms in the agri-food system? • What is the difference between science and technology? • What is the role of business management in the success of the agri-food system?
Discussion Questions • Identify the three major sectors of the agri-food system. Describe the evolution of agriculture into the agri-food system. • Describe the role of export markets and how they have changed in the past 25 years. • Describe the production sector’s environmental record. • Describe what you see as the future of the agri-food system in meeting the food needs of the world’s population and as a place to work. • Explain why you are optimistic or pessimistic about the agri-food system’s ability to produce enough food to feed a hungry world. What are the biggest challenges it will face in achieving this crucial goal?