Polymerization
600 likes | 792 Vues
Polymerization. Polymers are macromolecules. Many of them have formula weights in the thousands. The word polymer is derived from Greek. Poly means many . Mer comes from meros meaning parts.

Polymerization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Polymerization Polymers are macromolecules. Many of them have formula weights in the thousands. The word polymer is derived from Greek. Polymeans many. Mer comes from meros meaning parts. Polymers consist of many smaller molecules called monomers that are connected to form the larger macromolecule.
Natural Polymers Many natural substances exist as polymers including • Starch • Cotton (cellulose) • Wood (cellulose) • Proteins
Celluloid Celluloid, produced by treating natural cellulose with nitric acid, was one of the earliest synthetic polymers. Cellulose nitrate was used for billiard balls, men’s fashion collars, and movie film. Celluloid still has uses today. The first completely synthetic polymers were phenol-formaldehyde resins.
Polyethylene Perhaps the most common synthetic polymer is the plastic, polyethylene.
Polyethylene High density polyethylene (HDPE) exists as mostly linear molecules that pack closely together. It is used for milk jugs, bottle caps, toys, etc. Low density polyethylene(LDPE) is a more highly branched form of polyethylene. It is used to make plastic bags, plastic films, electric wire insulation, etc.
Polyethylene These two bottles, both made of polyethylene, were heated in the same oven for the same length of time. Which is made of HDPE and which is made of LDPE?
Thermoplastic and Thermosetting Polymers Thermoplastic polymers will soften upon heating. Polyethylene is one such polymer. Thermosetting polymers were heated to harden when they were formed. They will not soften upon heating, but will discolor and decompose.
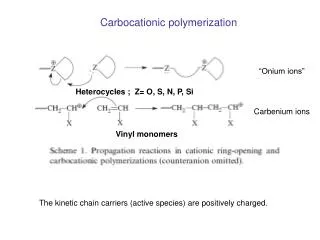
Addition Polymers Addition polymerization occurs when monomers add to one another in such a way that the resulting molecule contains all atoms that are present in the monomers. Addition polymers are all derivates of polyethylene.
Addition Polymers Polystyrene
Addition Polymers Polystyrene
Addition Polymers Polyvinyl Chloride
Addition Polymers Polyvinyl Chloride
Addition Polymers Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
Addition Polymers Conducting Polymers: Polyacetylene contains conjugated double bonds and can conduct electricity.
Molding Plastics Plasticmaterials can be made to flow under heat and pressure. Compression molding: Heat and pressure are applied directly to the polymer powder in the mold cavity. Injection molding: The plastic is melted and forced by a plunger into cold molds to set.
Molding Plastics Extrusion molding: Process during which a molten polymer is extruded through a die in continuous form to be cut into lengths or coiled. Blow molding: Process during which a “bubble” of molten polymer is blown up like a balloon inside a hollow mold. This is how bottles are formed.
Rubber and Other Elastomers Elastomersare polymers that will elongate when subjected to a tensile force. They will return to the original shape when the force is removed. Rubber is an elastomer. Natural rubber is composed of isoprene units. Isoprene is polymerized into polyisoprene (rubber).
Rubber and Other Elastomers Natural rubber is soft and tacky when hot. Reacting it with sulfur cross-links the polyisoprene and makes the rubber harder. This process is known as vulcanization and was discovered by Charles Goodyear.
Synthetic Rubber Synthetic rubber is similar to polyisoprene. One example is polybutadiene.
Synthetic Rubber Neoprene is very similar to polybutadiene, but contains chlorine in place of the methyl group. It is more resistant to solvents like oil and gasoline.
Synthetic Rubber Another synthetic rubber is styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR). SBR is a copolymer of styrene (25%) and butadiene (75%). It is tougher and more resistant to oxidation than natural rubber, but its mechanical properties are less satisfactory.
Polymers in Paints Elastomers are often used as binders in paints. Paints made with elastomeric binders are more resistant to cracking. Latex paints are such a product. These paints use water as a solvent and are more “environmentally friendly” than oil-based paints.
Condensation Polymers In condensation polymerization, small molecules such as water, alcohols, ammonia, or HCl are released as by-products.
Condensation Polymers Nylonis a polyamide. Most nylon is manufactured as fibers.
Condensation Polymers Polyesters are condensation polymers made from molecules containing alcohol and carboxylic acid functional groups. The linkage is an ester.
Condensation Polymers Phenol-formaldehyde resin was the first synthetic polymer. It was known as Bakelite in honor of its discoverer, Leo Baekeland. Leo Baekeland received a patent in 1909 for this polymer.
Condensation Polymers Formaldehyde can be condensed with urea to make urea-formaldehyde resins and with melamine to form melamine-formaldehyde resins.
Condensation Polymers Polycarbonates are tough, clear polymers used in protective helmets, safety glasses, and dental crowns.
Condensation Polymers Polyurethanes are similar to nylon. They may be elastomers or tough and rigid, depending on the monomers used. Polyurethanes are used in foam rubber, skate wheels, and tough furniture finishes.
Condensation Polymers Epoxy resins are often sold as two-part liquids. They make durable, clear coatings and are an excellent adhesive. They are very strong when cross-linked.
Composite Materials Composite materials are composed of high-strength fibers (i.e., fiberglass, graphite, or ceramic fibers) held in a polymeric matrix. Examples of composite materials include boat hulls, tennis rackets, automobile panels, fishing rods, etc.
Silicones Silicones are polymers that contain silicon rather than carbon. An example is polysiloxane.
Silicones Silicone polymers take many forms depending on their structure and degree of cross-linking. They can be in the form of liquid oils, gels, synthetic rubber elastomers, etc.
Properties of Polymers Polymers have very high molecular weights. Since the strength of intermolecular forces increases with molecular weight, polymeric materials exhibit very strong intermolecular forces. For these reasons, polymeric materials exist as strong fibers and polymers form viscous solutions.
Properties of Polymers The molecules of crystalline polymers line up in neat rows forming fibers of great strength. Crystalline polymers tend to be very rigid. Amorphous polymers, on the other hand, have molecules that are randomly tangled. Amorphous polymers tend to be soft and rubbery.
Properties of Polymers The glass transition temperature (Tg) is the temperature above which the polymer is tough and rubbery, and below which it is like glass―hard, brittle, and stiff.
Properties of Polymers Some synthetic polymers can be converted to fibers. Many can exhibit properties that are superior to natural fibers. The majority of fibers and fabrics used in the United States are synthetic.
Plastics and the Environment Most plastics do not decompose readily in the natural environment. Unwanted plastic waste can be dealt with by disposal in landfills, incineration, biodegradation, and recycling.
Disposal of Plastics Landfills Plastics make up 11% by mass of solid waste and 20% by volume. More than half of all solid waste ends up in landfills. Landfill space is becoming increasingly difficult to obtain.
Disposal of Plastics Incineration Many plastic materials have significant fuel value and incineration of solid waste, along with using the heat energy to generate electricity, is attractive. However, the combustion of plastics and rubbers is not without problems. Many of these materials release toxic gases when combusted. PVC plastic, for instance, releases HCl gas when burned.
Disposal of Plastics Degradable Plastics About half of our waste plastic comes from packaging. Expect to see more biodegradable and photodegradable plastics used for packaging in the near future.
Disposal of Plastics Recycling Over the long term, recycling may be the best way of dealing with waste plastics. Recycled plastics can be separated into the various types, chopped into flakes, melted, and remolded or spun into fibers.
Plastics and Fire Hazards Many people are injured each year due to accidental ignition of plastics. Federal regulations require that children’s sleepwear be made of flame retardant materials. Because some plastics release toxic gases during combustion, firefighters must protect themselves from these toxic fumes.
Plasticizers and Pollution Certain plastics, such as vinyl polymers, are stiff and brittle; plasticizers are used to make the materials more flexible. Many of these plasticizers have low volatility. Eventually these materials can become stiff and brittle as the plasticizers vaporize.
Plasticizers and Pollution Early plasticizers were polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB).
Plasticizers and Pollution More recent plasticizers are less toxic phthalate esters.
Plastics and the Future It is difficult to imagine the world without synthetic polymers and plastics. Many are made from petroleum or natural gas. Much research is being conducted on developing synthetic polymers from renewable resources. These materials represent both a challenge and hope for our future.