Hazard Recognition
520 likes | 1.95k Vues
Hazard Recognition. Instructional Goal: the participant will know what conditions in the waste site work environment could result in worker hazards and the importance of accident or exposure prevention. Hazard.

Hazard Recognition
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hazard Recognition Instructional Goal: the participant will know what conditions in the waste site work environment could result in worker hazards and the importance of accident or exposure prevention.
Hazard • any substance, situation, or condition that is capable of harming human health, property, or the environment
Risk • a measure of the probability and severity of a hazard to harm human health, property, or the environment Risk 0
Safety • defined as a judgment of the acceptability of risk
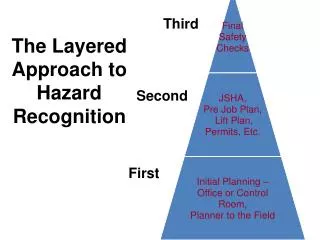
Site-Specific HASP • For safety of workers protective methods must be identified. • A model can be utilized to help recognize hazards involved in each task performed at the waste site. • Job Safety Analysis - Task specific
Job Hazard Steps • identify the site tasks that have the potential for injury or illness • list the steps involved to perform the task • use the steps to identify potential hazards associated with each step • determine the best method of protection
Hazard Recognition • an accurate assessment of all the hazards posed by the waste site is nearly impossible due to the large number and variety of substances
Chemical Hazard ID Systems • NFPA 704 System
Chemical Hazard ID Systems • DOT Labels
Hazard Recognition • ionizing radiation • chemical health hazard • chemical physical hazard • site and equipment hazards • environmental hazards • biological hazards A working environment may be characterized by any combination of the following hazards
Multiple hazards • Materials may have more than one hazard. • 1, primary hazard • 2 ,secondary hazard or subsidiary hazard. EXAMPLE: gasoline 1 fire hazard - flammable. 2 chemical health hazard - organic solvent NOTE: A worker must be aware of the multiple hazards of the materials they deal with to be protected from them.
Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation is radiation that has sufficient energy to remove electrons from atoms. • alpha • beta • gamma
Corrosive class substances polychlorinated biphenyls target organ poisons irritants mutagens teratogens asphyxiants carcinogens Chemical Health Hazard Health hazards cause adverse health effects and may be encountered on a waste site.
Chemical Physical Hazard Chemical hazards that cause physical injury.
Fire and Explosions • combustible liquids, flammable gases, aerosols and liquids • flammable solids • explosives; pyrophorics • oxidizers; organic peroxides • unstable/reactives; water reactives
Fire Prevention • only qualified personnel to monitor • use proper precautions and procedures • isolate potential ignition sources • use non-sparking, explosion proof equipment • follow established safe work practices
Oxygen Deficiency • displacement by another gas • consumption during a chemical reaction • combustion
Site and Equipment Hazards • holes or ditches • precariously positioned objects • sharp objects • slippery surfaces • steep grades • uneven terrain • unstable surfaces
Noise • effects of noise can include: • workers being startled, annoyed, or distracted • physical damage to the ear, pain, and temporary or permanent hearing loss • inability to communicate, interference
Electrical Hazards • overhead power lines • downed electrical lines • unmarked buried cables • defective insulation • charged capacitors • lightning
Prevent Electrical Accidents • regular inspection of equipment • training on power tools • use of low voltage and GFCIs • assure grounding • energy isolation (LOTO) • suspend work during electrical storms
Other Site Hazards • heavy equipment • PPE • power tools • lifting and moving drums/containers • slips, trips, falls • excavation hazards
Environmental conditions posed by the site. Environmental Hazards
Heat Stress • avoid overprotection • train personnel that will wear PPE • frequently monitor personnel • carefully schedule work and rest periods • drink plenty of fluids
Normal 98.6 Shivering 95 Loss of muscle control 92 88 Possible Death Hypothermia
Cold Exposure Prevention To guard against these hazards: • Wear appropriate clothing. • Have warm shelter readily available. • Carefully schedule work and rest periods. • Monitor workers' physical conditions.
Cold Exposure Treatment • Frost-damaged areas should be treated as follows: • Seek medical attention immediately. • Rewarm the frozen part quickly by immersing it in warm water. • Do NOT allow the victim to walk on frozen feet. • Elevate the feet after warming. • Prevent contact between the injured part and any surface except a sterile bandage.
Other Environmental Hazards • Plants that cause severe allergic reactions in some people. (poison ivy) • Venomous insects that can cause severe allergic reactions in some people. (hornets, wasps and bees) • Snake and animal bites. • Insect bites can cause severe illness. (ticks and spiders)
Biological Hazards • Pathogens • cholera • typhoid • Bloodborne diseases • hepatitis B virus (HBV) • human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
Minimize Exposure • Do not clean up blood or body fluids unless you have been trained. • Know what to do before an emergency occurs. • Be sure to wash your hands and remove any PPE before eating, drinking, smoking, or handling contact lenses.