Understanding Polygons: Definitions, Types, and Properties
90 likes | 230 Vues
This section explores the fundamental concepts of polygons, focusing on definitions and classifications. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional shape with straight sides. We distinguish between convex and concave polygons based on their interior points. The section also covers specific types of polygons, including equilateral and equiangular polygons, leading to the definition of regular polygons, which are both equilateral and equiangular. Examples illustrate how to identify and classify polygons according to their sides, helping learners understand the geometric principles behind shapes like triangles, quadrilaterals, and hexagons.

Understanding Polygons: Definitions, Types, and Properties
E N D
Presentation Transcript
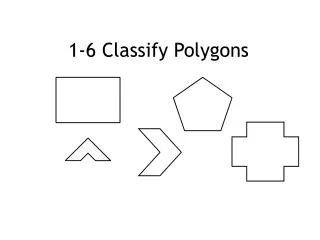
Classify Polygons Section 1.6
Vocabulary A polygon is a closed two-dimensional shape with straight sides.
Vocabulary A polygon is convex if no line that contains a side of the polygon contains a point in the interior of the polygon. A polygon that is not convex is called concave.
Vocabulary In an equilateral polygon, all sides are congruent. In an equiangular polygon, all angles in the interior of the polygon are congruent. A regular polygon is a convex polygon that is both equilateral and equiangular.
Vocabulary 3 sides Triangle 4 sides Quadrilateral 5 sides Pentagon 6 sides Hexagon 7 sides Heptagon 8 sides Octagon 9 sides Nonagon 10 sides Decagon 11 sides Undecagon 12 sides Dodecagon n sides n-gon
a. b. c. d. a. Some segments intersect more than two segments, so it is not a polygon. The figure is a convex polygon. b. Part of the figure is not a segment, so it is not a polygon. c. d. The figure is a concave polygon. EXAMPLE 1 Identify polygons Tell whether the figure is a polygon and whether it is convex or concave. SOLUTION
a. b. a. The polygon has 6 sides. It is equilateral and equiangular, so it is a regular hexagon. b. The polygon has 4 sides, so it is a quadrilateral. It is not equilateral or equiangular, so it is not regular. EXAMPLE 2 Classify polygons Classify the polygon by the number of sides. Tell whether the polygon is equilateral, equiangular, or regular. Explain your reasoning. SOLUTION
A table is shaped like a regular hexagon.The expressions shown represent side lengths of the hexagonal table. Find the length of a side. ALGEBRA 3x + 6 4x – 2 = 6 x – 2 = 8 x = EXAMPLE 3 Find side lengths SOLUTION First, write and solve an equation to find the value of x. Use the fact that the sides of a regular hexagon are congruent. Write equation. Subtract 3x from each side. Add 2 to each side.
Assignment • P. 44: 3-29(odds)