Understanding Complex Traits and Pedigrees: Genetics, Inheritance, and Sex-Influenced Characteristics
70 likes | 197 Vues
This comprehensive overview explores the intricacies of complex traits in genetics, highlighting characteristics that arise from multiple genes, such as eye and hair color, height, and more. It differentiates between sex-influenced and sex-linked traits, using male pattern baldness as a prime example. The guide also explains important concepts like complete dominance, codominance, and pedigrees, which are essential for tracking hereditary traits and disorders, such as Tay-Sachs disease. Discover how these traits are passed through generations and their implications for family genetics.

Understanding Complex Traits and Pedigrees: Genetics, Inheritance, and Sex-Influenced Characteristics
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Other Traits and Pedigrees Genetics
Complex Characteristics and Sex Influenced Traits • Complex Characteristics • Characteristics that are due to more than one gene. • Eye color, hair color, skin color, height, etc. • Most characteristics where there is a wide range of possibilities. • Sex Influenced Traits • Not the same as sex link traits • Influenced traits are carried on autosomes • They are influenced due to the hormones that each gender produces • Male Pattern Baldness – A trait where males start going. This trait is actually a dominant trait and only one allele is needed to have it, in men. However, it is sex influenced. Women actually need 2 dominant alleles in order to express this trait.
Helpful Reminders • Complete Dominance • Can be done as an autosomal trait (A and a as alleles) or sex linked (XR, Xr and Y). • Only two phenotypes exist and one can cover up the other. • If it is autosomal both men and woman can be hybrid, carriers, or heterozygotes • Codominance • Two different letters for the alleles (R and B), both capital, look for spots, stripes, or speckles • Incomplete Dominance • Same letter for the alleles (R and r), look for a blend (red + white = pink); 3 phenotypes • Dihybrid • FOIL! • Sex Linked • Use the sex chromosomes (XR, Xr and Y) • Woman can be carriers; Men cannot be carriers, they either have it or they don’t • Blood • Multiple alleles (IA, IB, and io); 4 phenotypes
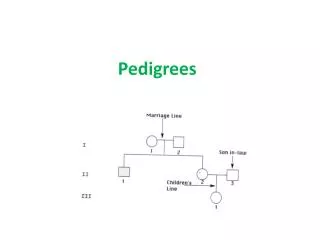
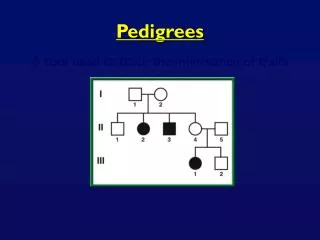
Pedigrees • A way to follow a family lineage • Convenient for looking at traits as they pass on from parent to offspring, especially in the case of a lethal or debilitating disorder
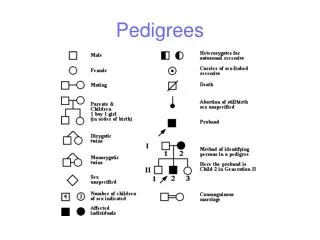
Pedigrees A circle represents a female. A shaded in circle represents a female that has a specific trait. A square represents a male. A shaded in square represents a male that has a specific trait. A horizontal line indicates two individuals that have produced offspring A vertical line coming down indicates the offspring that they have produced. Siblings are connected by a horizontal line that drops down into vertical lines. Offspring go in birth order.
Steve Amy Josh Jennifer Ben Allen Christina How many females are in this pedigree? How many males are in this pedigree? How many children do Steve and Amy have? Who is the 2nd born child of Steve and Amy? How is Sally related to Amy? 4 4 4 Allen Sally is her granddaughter Sally
Tay-Sachs Disease is an autosomal recessive disorder. It is caused by the absence of the enzyme Hex-A. This causes cells to become damaged. This will result in progressive neurological disorders eventually leading to death. Steve Amy Josh Jennifer Ben Allen Christina Six months are Ben and Christina had Sally, they discovered that Sally had Tay-Sachs disease. Since it is an autosomal recessive disorder: What does this mean about Ben and Christina? If they conceive another child, what would be the chance that they would also have Tay-Sachs? Sally They are carriers. 25%