Electronic Configuration
220 likes | 728 Vues
Electronic Configuration. Energy Levels. Energy levels are called principal energy levels and are given numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 These principal energy levels contain sub-levels which are assigned the letters s, p, d and f. 4f. 4d. 4. 4p. 4s. Energy. 3d. 3p. 3. 3s. 2p. 2.

Electronic Configuration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Energy Levels • Energy levels are called principal energy levels and are given numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 • These principal energy levels contain sub-levels which are assigned the letters s, p, d and f
4f 4d 4 4p 4s Energy 3d 3p 3 3s 2p 2 2s 1 1s
Each type of sub-level can hold a different number of electrons
4f14 4d10 4 4p6 4s2 Energy 3d10 3p6 3 3s2 2p6 2 2s2 1 1s2
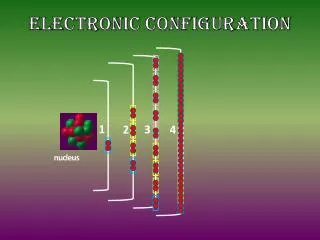
Electron Orbitals • Electrons are constantly moving, however, orbitals are regions where is it highly likely an electron might be found • The energy sub-levels are made up of orbitals, each of which can hold a maximum of 2 e-.
Electron Orbitals • The orbitals in different sub-levels have different shapes
Each orbital can hold 2 e-. The p sub-shell contains 6 e-
Each type of sub-level can hold a different number of electrons
Energy Levels Orbital 4p Energy 3d 4s 3p 3s Sub- levels 2p 2s Principal Energy levels 1s
Drawing Electron Configurations • Electrons are drawn as single headed arrows. • The direction of the arrows represent the spin of the electron
Hund’s Rule • Electrons occupy orbitals as unpaired e-. The e- are only paired when there are no more empty orbitals available in that sub-level. This is Hunds Rule • Paired electrons will have opposite spin as this reduces the mutual repulsion between the paired e-.
Energy Level Diagrams 4p Energy 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s Na 11e- 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s1 1s
Energy Level Diagrams 4p Energy 3d 4s 3p 3s 2p 2s 1s
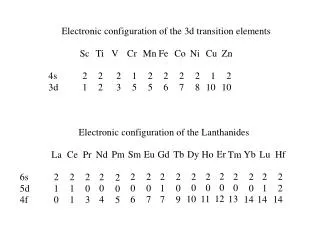
Anomalous Electron Configurations • Chromium has the electron configuration • 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d5 4s1 • NOT 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d4 4s2 • The outer sub-level is half full, this is a more stable arrangement.
Anomalous Electron Configurations • Copper is • 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d10 4s1 • NOT 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 4s2 • The outer sub-level is full, this is a more stable arrangement.
Electronic Structure of Ions • Positive Ions – formed by the loss of e- Na Atom Na+ion • 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 1s2 2s2 2p6 • Negative Ions – formed by the gain of e- O Atom O2- ion • 1s2 2s2 2p4 1s2 2s2 2p6
Structure of Transition Metal Ions • With the transition metals it is the 4s electrons are lost first when they form ions • Ti 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6 3d24s2 • Ti2+ 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6 3d2 • Cr 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6 3d54s1 • Cr3+ 1s2 2s2 2p63s2 3p6 3d3