Civilization Begins Chapter 1
140 likes | 320 Vues
Civilization Begins Chapter 1. Prehistory – 3000 B.C. Measurement of Time. Prehistory to 0 B.C. – Before Christ or… B.C.E. – B efore Common Era Year 1 to present is referred to as: A.D. – Anno Domini or… C.E – common era. 1.1. The Geographer . Study people & their environment

Civilization Begins Chapter 1
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Civilization BeginsChapter 1 Prehistory – 3000 B.C.
Measurement of Time Prehistory to 0 • B.C. – Before Christ or… • B.C.E.– Before Common Era Year 1 to present is referred to as: • A.D. –Anno Domini or… • C.E – common era
1.1 The Geographer • Study people & their environment • Study five major themes: • Location - where a place is on the surface of the Earth • Interaction - how people have shaped and been shaped by the places where they lived • Movement - of people, goods, and ideas • Place - physical & human characteristics of a location • Region - places with similar unifying physical, economic, or cultural features.
The Archeologists… • Study Prehistory - before there was writing. • Study artifacts - objects made by people, such as tools, weapons, pottery, clothing, and jewelry.
The Historian • Study written evidence such as letters or tax records and visual evidence such as photographs or films to reconstruct the past. • Evaluate information for reliability
1.2 Paleolithic Age • Old Stone Age • Lasted until ~10,000 BCE • Hunter/gatherers or nomads. • Made clothes & tools (i.e. spears & axes from natural materials) • Built fires • Developed spoken languages • Religions began Sungir, Russia, buried some 25,000 years ago
Neolithic Age • New Stone Age • Learned to farm • Plant seeds & domesticated animals • Transformed our existence • Appx. 5,000 years ago, these advances led to the rise of civilizations. • Social hierarchy (leader, farmers, etc.) • Accumulation of personal property • New technologies
Homework: • Read the article, “Pros and Cons of Farming.” Hunting/Gathering vs Farming Pros Cons
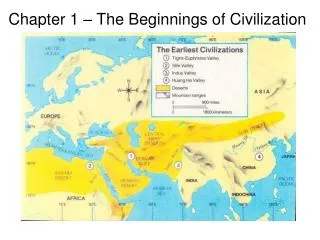
Beginnings of Civilizations Cities first arose in river valleys because: • Water • Farming • Renewable soil • Animals • Transportation
Civilizations Emerge Farmers began cultivating lands along river valleys & producing surplus Surpluses helped populations expand As population grew, villages swelled into cities
8 features common to early civs: • Cities • In fertile areas (near rivers) producing a food surplus. • Well-organized central governments • Needed to maintain order and the surplus • Divine Right • Bureaucracy developed • Complex religions • Polytheistic, believing in many gods • Controlling the natural forces and human activities • People created ceremonies, temples and priests to intervene with the gods on behalf of the people • Job specialization • Artisans, priests, farmers, weapons maker and soldiers
Features 5. Social classes • The importance of the persons job ranked them socially 6. Arts and architecture • Temples to the gods • Places for the rulers 7. Public works to benefit the city • Defensive walls, irrigation systems, roads and bridges 8. Writing • Pictograms • Leaders needed to keep records