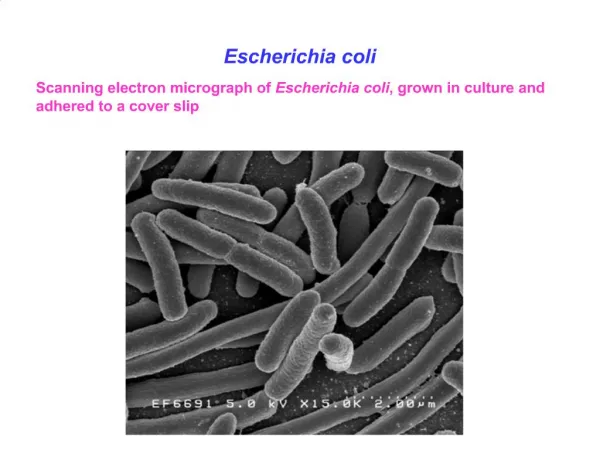
Balantidium coli
980 likes | 5.42k Vues
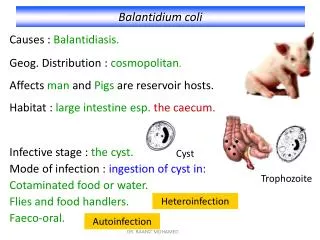
Balantidium coli. Causes : Balantidiasis. Geog. Distribution : cosmopolitan . Affects man and Pigs are reservoir hosts. Habitat : large intestine esp. the caecum. Infective stage : the cyst. Mode of infection : ingestion of cyst in: Cotaminated food or water.

Balantidium coli
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Balantidium coli Causes : Balantidiasis. Geog. Distribution : cosmopolitan. Affects man and Pigs are reservoir hosts. Habitat : large intestine esp.the caecum. Infective stage : the cyst. Mode of infection : ingestion of cystin: Cotaminated food or water. Flies and food handlers. Faeco-oral. Cyst Trophozoite Heteroinfection Autoinfection DR. RAAFAT MOHAMED
Life Cycle of Balantidium coliinside human colon Pass out in stool In the lumen Trophozoites multiply by both Transverse binary fission & Conjugation Cyst enters with food Attached to mucosa trophozoite Mucosa of large intestine DR. RAAFAT MOHAMED
Multiplication of Balantidiumin large intestine Trophozoites multiply by: transverse binary fission Trophozoites multiply by: conjugation between large andsmall trophozoites. Exchange of some nuclear fragments Fragmentation of nuclei DR. RAAFAT MOHAMED
Pathogenesis and Clinical picture Trophozoites invade mucosa by: - hyaluronidase enzyme. - boring action of cilia. Formation of flask-shaped ulcer. Secondary bacterial infection. Symptoms of dysentery. Complications: - Haemorrhage. - Perforation. - Peritonitis. - Appendicitis. DR. RAAFAT MOHAMED
Diagnosis Stool examination several times. Pass in diarrhoeic stool Pass in formed stool Treatment Metronidazole OR Oxytetracycline Control Care in disposal of pig’s excreta DR. RAAFAT MOHAMED
Check for understanding State true or false • Balantidium coli lives in the duodenum of infected patient. • Balantidium coli forms a flask-shaped ulcer in mucosa. • Infection with B.coli occurs through eating pork. • Infection with B.colicauses tenesmus and abd. pain. • Autoinfection can occur in balantidiasis. F B.coli lives in the caecum of infected patient T F Infection occurs through eating contaminated food or water. T T DR. RAAFAT MOHAMED