Predicting Solar Magnetic Field at Earth
170 likes | 327 Vues
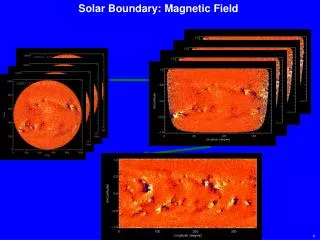
Predicting Solar Magnetic Field at Earth. Dusan Odstrcil George Mason University & NASA/GSFC/Space Weather Laboratory. MURI/NADIR Workshop Boulder, CO October 27-28, 2010. Background Solar Wind by FR Coronal Maps. MAS and WSA coronal FR maps provide Br only

Predicting Solar Magnetic Field at Earth
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Predicting Solar Magnetic Field at Earth Dusan Odstrcil George Mason University & NASA/GSFC/Space Weather Laboratory MURI/NADIR Workshop Boulder, CO October 27-28, 2010
Background Solar Wind by FR Coronal Maps • MAS and WSA coronal FR maps provide Br only • ENLIL introduces Bphi at the inner boundary • Initially Btheta = 0; weak Bz by stream interaction and seasonal effect
Transient Disturbances Modeling of the origin of CMEs is still in the research phases and it is not expected that real events can be routinely simulated in near future. Therefore, we have developed an intermediate modeling system which uses the WSA coronal maps, fitted coronagraph observations, specifies 3D ejecta, and drives 3D numerical code ENLIL.
“External” Bz Periods – Shock Compression Shock to north, positive IMF: + Shock to north, negative IMF: - Shock to south, positive IMF: - Shock to south, negative IMF: +
“External” Bz Periods – ICME Draping Above ICME center, positive IMF: - + Above ICME center, negative IMF: + - Below ICME center, positive IMF: + - Below ICME center, negative IMF: - +
May 12, 1997 – Interplanetary CME ENLIL heliospheric model (GMU-NASA /GSFC) MAS coronal model (PSI) Self-consistent end-to-end numerical simulation of space weather event (NSF/CISM effort in progress)
2008 April 26 CME with Rope Model ( Thernisien et al., 2009 ) ( WSA-1.6-GONG-CR2069 )
Conclusion • Solar Wind – Fully-automatic forecasting (Weak Bz events only) • ICMEs/fitted coronagraph observations – Semi-automatic forecasting (Moderate Bz by draping and shock compression) • ICMEs/self-consistent eruption– In active research (strong Bz) • ICMEs/semi-empirical flux ropes – Semi-automatic forecasting might ne possible (strong Bz)