System Design
120 likes | 181 Vues
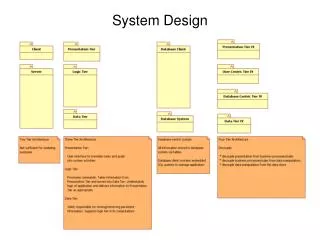
for Home Automaton. System Design. Design Goals. Performance Criteria Server prioritizes client requests to provide quick response time to critical requests. E.g. Device state changes supersede image transfers.

System Design
E N D
Presentation Transcript
for Home Automaton System Design
Design Goals • Performance Criteria • Server prioritizes client requests to provide quick response time to critical requests. • E.g. Device state changes supersede image transfers. • Client is multi-threaded to allow simultaneous server communication and user interaction. Server is a single-threaded state machine. • One zone will be held in memory at any given time to limit memory consumption.
Design Goals • Dependability Criteria • Errors in server connection will be reported to the user. • Requests are given an encrypted identifier. Server reports success or failure to client with identifier. • Out-of-order transmissions generate errors and the connection is terminated to handle packet spoofing.
Design Goals • Cost Criteria • Open-source; free for all. Yee-Ha! • Maintenance/Extendability Criteria • Extendable to multiple device types. • Server will be able to communicate with a client on any platform. • End User Criteria • Easy point-and-click user interface.
Hardware/Software Mapping • Client • C#, Open GL • Server • C++ • Protocol • TCP/IP Sockets
Persistent Data Management • Zones will be stored in data files managed by data structures. • Users will be stored in a data file on the server • Server configuration will also be stored in a data file
Access Control • There are two types of users: Administrator and Occupant. • Administrator has full access to all features of the client and server. • Occupant has access only to change device states. • Both user types are authenticated with a username and password.
Software Control • The server will operate on a procedure-driven state machine with a single-threaded loop handling all input/output and device control operations. • The client will operate on an event-driven model with multiple threads (GUI & Network)
Boundary Conditions • Establish Server Connection • User is authenticated. All devices (real and virtual) and the image file for the root zone are downloaded to the client • Disconnect From Server • Server request queue is flushed and executed, while errors are reported to the client.
Boundary Conditions • Connection Unexpectedly Terminated • Server processes all requests in its queue and stores errors in a log file. • Client reports an error to the user and offers to reconnect. Upon reconnection, Client will be updated with the current devices states.