Set Design at Delphi
100 likes | 279 Vues
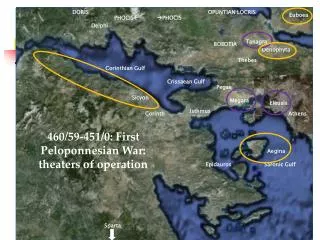
Set Design at Delphi. Understanding Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic Greek Art . Courtesy of Archivision.com. Utilize elements of Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic in your set design . Archaic. 600 BCE- 480 BCE Arts developed rapidly during this period

Set Design at Delphi
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Set Design at Delphi Understanding Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic Greek Art Courtesy of Archivision.com
Utilize elements of Archaic, Classical, and Hellenistic in your set design
Archaic • 600 BCE- 480 BCE • Arts developed rapidly during this period • In architecture stone and marble replaced the earlier mud brick and wood construction
Archaic • Doric and Ionic Orders developed during this period • Kore and Kouros sculptures • Anatomy of sculpture uses ridges and grooves to form geometric patterns • Archaic smile, arms usually rigidly placed at the sculptures sides • One leg of sculptures is slightly in front of the other
Classical Period • 479 BCE - 322 BCE • Ideal and the General • Aloof expressions on sculptures • This period is framed by two major events: The defeat of the Persians in 479 BCE and the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BCE Antinous, Delphi Museum, Greece
Classical Period • Adages carved into the Temple of Apollo such as: • “Man is the measure of all things” • “Know thyself” • “Nothing in excess”
Classical Period • Humanism • Rationalism • Idealism
Humanism Imagined their gods looked like perfect human beings Apollo for example is the exemplified Greek ideal: body and mind in balance • Rationalism Greeks at this time valued reason over emotion. The Greeks saw aspects of life including the arts as having meaning and pattern. Cannon of proportions • IDEALISM The True, The Good, The Beautiful
Hellenistic Period • 323 BCE - 30 BCE • Individual and Specific • Turns from subject matter of heroic to the everyday • Sculptures begin to show human emotion • Appeals to the senses with dramatic poses and subjects • Architecture begins to reflect taste for high drama
Resources/Contributions: • Stokstad, Marilyn. Art History: Second Edition Volume One. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall Inc., 2002.