MYERS-BRIGGS TYPES
380 likes | 555 Vues
Explore the key concepts of personality types, focusing on dimensions like Extraversion and Introversion. This guide delves into how individuals perceive their world, whether it revolves around people or ideas. The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) offers insights into decision-making processes based on Thinking versus Feeling and the preference between Judging and Perceiving. Understand how different personality types interact in work settings and how they contribute uniquely to teams. Gain a better grasp of yourself and others through this valuable framework.

MYERS-BRIGGS TYPES
E N D
Presentation Transcript
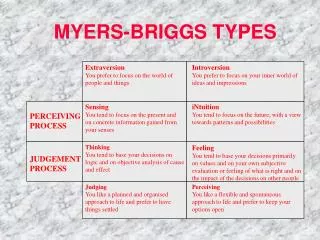
Extraversion You prefer to focus on the world of people and things Introversion You prefer to focus on your inner world of ideas and impressions Sensing You tend to focus on the present and on concrete information gained from your senses iNtuition You tend to focus on the future, with a view towards patterns and possibilities PERCEIVING PROCESS Thinking You tend to base your decisions on logic and on objective analysis of cause and effect Feeling You tend to base your decisions primarily on values and on your own subjective evaluation or feeling of what is right and on the impact of the decisions on other people JUDGEMENT PROCESS Judging You like a planned and organised approach to life and prefer to have things settled Perceiving You like a flexible and spontaneous approach to life and prefer to keep your options open MYERS-BRIGGS TYPES
MYERS-BRIGGS HIERARCHY DOMINANT AUXILIARY TERTIARY INFERIOR CONSCIOUS UNCONSCIOUS
THE DIRECTION OF THE DOMINANT If Extraverted Most conscious World of People and Things DOMINANT Inner World of Ideas and Impressions AUXILIARY TERTIARY INFERIOR Least conscious of
THE DIRECTION OF THE DOMINANT If Extraverted EXAMPLE E NTJ Most conscious World of People and Things THINKING Inner World of Ideas and Impressions INTUITION SENSING FEELING Least conscious of
THE DIRECTION OF THE DOMINANT If Extraverted EXAMPLE E NTP Most conscious World of People and Things INTUITION Inner World of Ideas and Impressions THINKING FEELING SENSING Least conscious of
THE DIRECTION OF THE DOMINANT If Introverted World of People and Things DOMINANT Inner World of Ideas and Impressions Most conscious AUXILIARY TERTIARY Least conscious of INFERIOR
THE DIRECTION OF THE DOMINANT If Introverted EXAMPLE I NTJ World of People and Things INTUITION Inner World of Ideas and Impressions Most conscious DOMINANT THINKING FEELING Least conscious of SENSING
THE DIRECTION OF THE DOMINANT If Introverted EXAMPLE I NTP World of People and Things THINKING Inner World of Ideas and Impressions Most conscious DOMINANT INTUITION SENSING Least conscious of FEELING
THE PROCESS OF MAKING SENSE TO OTHERS THE IMPACT YOU HAVE THE ACTION YOU TAKE THE THOUGHTS YOU HAVE WHAT YOU THINK/CONCLUDE PERCEIVING /JUDGING TELL WHAT YOU ARE TRYING TO DO
THE PROCESS OF MAKING SENSE TO OTHERS THE IMPACT YOU HAVE THE ACTION YOU TAKE THE THOUGHTS YOU HAVE WHAT YOU THINK/CONCLUDE PERCEIVING /JUDGING LISTEN WHAT YOU ARE TRYING TO DO
EXTRAVERTS at WORK • like variety and action • often good at greeting people • sometimes impatient with long/slow tasks • interested in how others do their jobs • enjoy talking on the phone • like to have people around • may act quickly, sometimes without thinking • may prefer talking to writing • like learning by talking it through
INTROVERTS at WORK • like quiet for concentration • have trouble remembering names and faces • can work on same project for a long time without interruption • interested in the idea behind the job • dislike telephone interruptions • think before they act - sometimes without acting • work alone contentedly • may prefer writing to talking • may prefer to learn through reading rather than talking or experiencing
SENSING TYPES at WORK • aware of the uniqueness of each event • focus on what works now • like an established way of doing things • enjoy applying what they have learned • work steadily, realistic about how long things take • reach conclusions step by step • not often inspired - may distrust inspiration when it happens • careful about the facts • may be good at precise work • can oversimplify a task • accept and work with reality
INTUITIVE TYPES at WORK • aware of new challenges and possibilities • focus on how things could be improved • dislike doing the same thing repeatedly • enjoy learning new skills • work in bursts of energy powered by enthusiasm, with slack periods in between • may leap to conclusions quickly • follow their inspirations and hunches • may get facts a bit wrong • dislike taking time for precision • can over complexify a task • ask why things are as they are
THINKING TYPES at WORK • good at putting things in logical order • respond more to people's ideas than to their feelings • expect or predict logical outcomes • need to be treated fairly • tend to be firm and tough-minded • able to reprimand or fire people when necessary • may hurt people's feelings without noticing it • talent for analysing a problem or situation
FEELING TYPES at WORK • like harmony and try to make it happen • respond to people's values as much as to their ideas • can see how choices affect people • need occasional praise • tend to be sympathetic • dislike telling people unpleasant things • enjoy pleasing people • interested in the person behind the job or idea
JUDGING TYPES at WORK • work best if they can plan - and follow the plan • like to get things settled and finished • may decide things too quickly • may dislike to interrupt their tasks for more urgent ones • tend to be satisfied once they reach a judgement on a thing/situation/person • want only the essentials necessary to begin the task • schedule projects so that each step gets done on time • Use lists as agenda for action
PERCEIVING TYPES at WORK • don't mind leaving things open for last minute changes • adapt well to changing situations • may have trouble making decisions - feeling they never have enough information • may start too many projects and have difficulty finishing them • may postpone unpleasant jobs • want to know all about a new job • get a lot done at the last minute under pressure of a deadline
PROBLEM SOLVING S (what are the facts?) N (what are the possibilities?) T (what’s the logical conclusion?) F (how does it impact the people? Is it consistent with our values?) J (plan and implement) P (remain open to new information; be prepared to adapt and change)
Communications Useful pointers to use when discussing tasks and trying toinfluence; explain;understand;present to: • Sensors • Be factual • Document successful applications • Reduce risk factors • Work out details in advance • Show why it makes sense • Intuitives • Give the global scheme • Don't let opportunity pass • Be confident and enthusiastic • Indicate challenges • Point out future benefits • Thinkers • Be logical • State principles involved • Stress competent handling of issue • Be well-organised • List the costs and benefits • Feelers • Mention others involved or affected • Be personable and friendly • Indicate how it is helpful • Tell why it's valuable • Show how it supports personal goals
EXTRAVERT managing/working with INTROVERT • draw them out on what they say (there is usually more behind the words) • allow them time to reflect • follow up discussion with a written note • will get a better contribution 1:1 or in a small group
INTROVERT managing/working with EXTRAVERT • talk things over to ensure understanding • expand on what you say - don't assume it is obvious • bring in other people • keep things moving and active
SENSING managing/working with INTUITION • ask them about the possibilities • get them to problem solve complex problems • ask them about trends and future direction • describe the overview first • indicate what your trying to achieve first • give them relevant detail later • be careful they don’t read more into what you say than you intend
INTUITION managing/working with SENSING • be specific, describe the current situation • elaborate on what you say, don’t expect them to spot the implications of what you say • build up the argument from the specifics • ask them to check detail particularly when it is important • get them to resolve problems that require patience and diligence • they mean what they say - not what you think they might mean!
THINKING managing/working with FEELING • ask them to forecast how people might react • ask them to conciliate when there is disagreement • ask them about the effects of the task on them - not just whether they understand the task • recognise that their ‘feel’ for what is rightisoften right even if they can’t justify it logically
FEELING managing/working with THINKING • recognise they need options and decisions to be grounded in evidence and logically sound • use them when you need someone to take a firm, intellectually rigorous stand • use them to evaluate and analyse options • try changing their minds by reviewing the evidence not challenging the conclusion
JUDGING managing/working with PERCEIVING • point out that although they can cope with less structure, others can’t! • emphasise that good project management needs discipline • ask them to deal with unexpected requests • they usually welcome interruptions - so ask! • accept that they often rely on last minute pressure to get things done • they can get side-tracked and may need to be brought back to task
PERCEIVING managing/working with JUDGING • ask them to prepare plans and organise tasks • give them good notice of requests - don’t leave it to the last minute • they look for decisions - make them explicit • they are focused on getting things done • they like to work with structure and organise their time
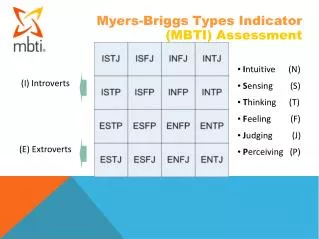
THE SIXTEEN TYPES% Distribution among Professionals judged as particularly Creative by their peers
MYERS-BRIGGS TYPES Italic = what you see Heavy bold = what is dominant
CHARACTERISTICS OF PARTICULAR COMBINATIONS NFs communicate in creative ways STs prefer proven methods SFs like to help others NTs like to debate challenging questions
CHARACTERISTICS OF PARTICULAR COMBINATIONS ISs are careful and attentive to detail ESs want to see and discuss practical results INs want to work with ideas and concepts ENs want to maximise variety
CHARACTERISTICS OF PARTICULAR COMBINATIONS SJs value responsibility and loyalty SPs value cleverness and timeliness NFs value inspiration and personal issues NTs value ingenuity and logic
IMPLICATIONS FOR WORK CULTURE • SJs value responsibility and loyalty • STs prefer proven methods • ESs want to see and discuss practical results • ISs want to be careful and attentive to details • SFs like to apply experience to help others • ENs want to maximise variety • INs want to work with ideas and principles • NTs value ingenuity and logic • NTs like to debate challenging questions • NFs value inspirations and want to add value for others