Phylum Apicomplexa
440 likes | 1.43k Vues
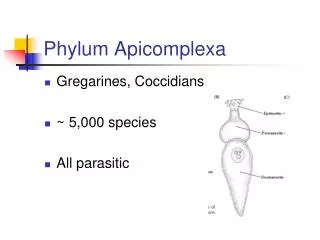
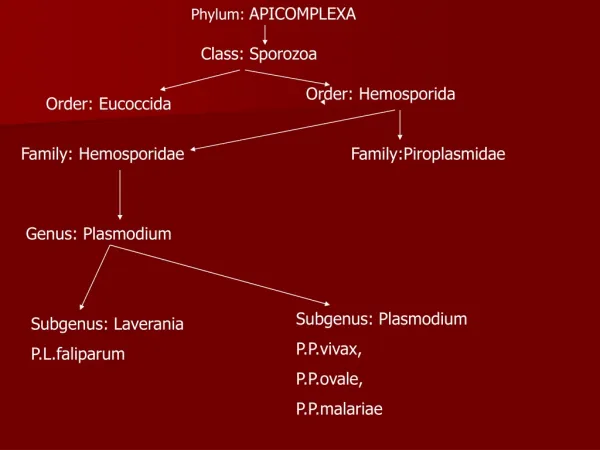
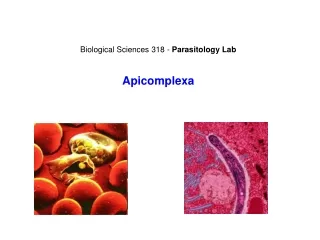
Phylum Apicomplexa. Gregarines, Coccidians ~ 5,000 species All parasitic. Apical complex. Organelles for attaching parasite to host cell Hooks/suckers. Plasmodium vivax. Causes malaria Kills 1-3 million / year Mostly in Africa Vector = mosquito.

Phylum Apicomplexa
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Phylum Apicomplexa • Gregarines, Coccidians • ~ 5,000 species • All parasitic
Apical complex • Organelles for attaching parasite to host cell • Hooks/suckers
Plasmodium vivax • Causes malaria • Kills 1-3 million / year • Mostly in Africa • Vector = mosquito
Gregarine: gut parasites of many invertebrates • Best known from arthropods • sporozoite
spores In beetle
Phylum Dinoflagellata • ~ 4,000 species described • Most unicellular, some are filamentous or colonial • Some planktonic, some symbiotic (w/ corals, other cnidarians)
Red tide caused by dinoflagellates • Discolored area of ocean with billions of dinoflagellates • Produce toxins, kill everything.
Two flagella: armor or not Ceratium
Dinoflagellates • Freshwater and marine • Osmoregulation by pusules • Tubules that open to outside • Autotrophic and heterotrophic • Switch • Many photo pigments
Repro • Asexual • Sexual: haploid cells divide, produce daughter cells = gametes • Forms cyst, resting stage
Phylum Rhizopoda: amebas • ~ 200 species • Most free-living, some endosymbiotic, some pathogenic • Pseudopodia in all
Entamoeba histolyticaAmebic dysentery • 4 nuclei - cyst found in fecal smear
Phylum Actinopoda • ~4,240 species • Radiolarians, Heliozoans, etc. • Most w/internal siliceous skeletons • Planktonic and benthic • Heterotrophic mostly (phagocytosis) • Binary fission, budding, sex rare
Actinopoda • “ray feet” = axopodia • Slender pseudopodia • Actinosphaerium
Foraminifera • ~ 40,000 species • All aquatic habitats • Some planktonic, most benthic • Tests form chalks, marble, limestone
Phylum Diplomonadida • Plasma membrane rigid from three microtubular roots • Most phagotrophic, feed on bacteria • Asexual, most form cysts
Giardia • No mitochondria, ER, or Golgi bodies • Warm climates mostly • In severe infections every cell in gut is covered by a parasite. • Coating of inside of intestine interferes with absorption
Phylum Chlorophyta • “Green algae” - green chloroplasts • Like plants • Some colonial • Some have lost photosynthesis = heterotrophs
Phylum Opalinida • Many rows of cilia - different than in ciliates • Reproduction is longitudinal (like flagellates), not transverse (ciliates) • ~ 150 species • Endosymbiotic in frog and toad gut
Phylum Opalinida • Sexual repro by synamy • Asexual = binary fission • Opalina
Protist Phylogeny • Origins ~ 2.5 bya • Evolution of eukaryotes? • Serial Endosymbiotic Theory (SET)