Intro to Forces and Motion
110 likes | 310 Vues
Intro to Forces and Motion. Ms. Graettinger Physical Science. What is a force?. Force is a push or pull on an object or by an object Force= mass x acceleration F=ma A force is that which changes or tends to change the state of rest or motion of a body. Newton’s 3 Laws.

Intro to Forces and Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Intro to Forces and Motion Ms. Graettinger Physical Science
What is a force? • Force is a push or pull on an object or by an object • Force= mass x acceleration • F=ma • A force is that which changes or tends to change the state of rest or motion of a body.
Newton’s 3 Laws • 1st : An object in motion stays in motion. An object at rest stays at rest--until an outside force acts upon it • 2nd : F=ma • 3rd : For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
The Force Equation • F = ma • Force = mass x acceleration • Mass is in kg • Acceleration is in m/s2 • Force is in Newtons (N)
Force Equation Example • How much force is needed to accelerate a 70-kg rider and her 200-kg motorcycle at 4 m/s2? • F=ma • F=(70kg + 200kg) x (4 m/s2) • F=1080 N
Falling Objects • Any two objects falling from the same distance, released at the same time, will land at the same time • Why is this?
Acceleration due to Gravity • Falling objects accelerate at 9.8m/s2 • Therefore, • Weight=m x a • W=m x 9.8m/s2
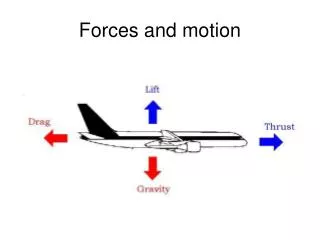
Air Resistance • The force air exerts on a moving object • If there is no force except for gravity, all objects will accelerate at a rate of 9.8 m/s2
Air Resistance • This force acts in the opposite direction to that of the objects motion • Air resistance pushes up while gravity pulls down
Classwork:Everyone must calculate how much they really weigh in Newtons.Conversion factor: 1kg=2.2 lb