Creating a Data Structure
130 likes | 346 Vues
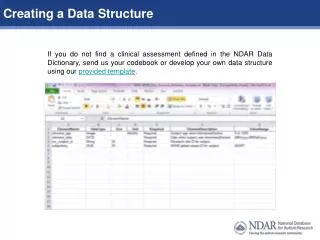
Creating a Data Structure. If you do not find a clinical assessment defined in the NDAR Data Dictionary, send us your codebook or develop your own data structure using our provided template . . Data Types. D ata elements fall into following categories :.

Creating a Data Structure
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Creating a Data Structure If you do not find a clinical assessment defined in the NDAR Data Dictionary, send us your codebook or develop your own data structure using our provided template.
Data Types Data elements fall into following categories: • Integer: a whole number (not a fractional number) that can be positive, negative, or zero • Float: a number that contains a floating decimal point • String: a text (a sequence of characters) • Date: MM/DD/YYYY • GUID: special subject’s identifier • File: file(s) linked to data being submitted
Value Ranges A value range is the acceptable values for a data element. Multiple values must be separated by a semicolon. Ranges of values should be separated with two colons. A valid value must match the data type of the data element. For example, if the data element is an integer, it is not appropriate to have a value range containing letters.
Formatting and Organization The following are required data elements and must be included in a data structure.
Formatting and Organization *from the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule – Module 2 Assessment scores always be listed as required elements.
Naming Elements Element names should be created based on a combination of the assessment name and question number. For longer assessments with multiple sections, we recommend including the title of the corresponding section. Element names are limited to 30 characters. *from the Early Childhood Behavior Questionnaire Assessment abbreviation Question number *from the Ages and Stages Questionnaires Section name Subject’s age and question number
Naming Elements *from the Background History Form *from Demographics When creating a new data structure, please reuse as many data elements as possible from the Data Dictionary.
Naming Elements To find existing elements, please refer to “Manage Data Elements” in the NDAR portal. Once logged into the portal, click on Data Dictionary in the Menu bar.
Naming Elements On the right sidebar, click on “Manage Data Elements.”
Naming Elements Here you can search through all of the existing elements.
Translation • If you have valid values in your system that are not in the NDAR Data Dictionary, we can create translations rules to accept your values. If you have an assessment defined in your system and have never used NDAR’s names, please use Alias Mapping to connect your names to NDAR’s.
Review Once complete, send us your txt or csv file for review. Please also provide a pdf version of the assessment with a description. Please let us know if you want to see your lab name associated with provided data structure.
Need Help? Each data structure is reviewed by NDAR staff prior to publication in the Data Dictionary. If you need assistance, please contact the NDAR Help Desk at NDARHelp@mail.nih.gov.