Animal Digestion
150 likes | 260 Vues
This PowerPoint presentation, originally created by Casey Okska and modified by the Georgia Agricultural Education Curriculum Office, delves into the essentials of animal digestion and nutrition. It covers the types of nutrients animals require, including carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals. The presentation explains the differences between ruminant and non-ruminant animals, feeding frequency, and the nutritional needs during different life stages. It also discusses how to balance rations using the Pearson square method, ensuring optimal animal health and productivity.

Animal Digestion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Animal Digestion Original Power Point Created by Casey Osksa Modified by Georgia Agricultural Education Curriculum Office June 2002
What are Nutrients? • parts of food which provide for growth, maintenance, body functions • Carbohydrates (CHO) • Fats • Proteins • Vitamins • Minerals • Water
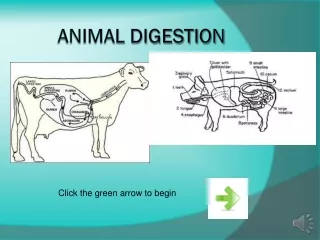
What is a Ruminant? • Animals with more than one stomach • Chew their cud (re-chew food) • Cows, sheep, goats • Cows have four stomachs • Alf has eight stomachs
Why don’t cattle need as much B vitamins? • Microorganisms in the stomach of the cow make their own B vitamins • Can also make some proteins if given the right kind of Nitrogen
NonRuminants • Foragers: Horse, rabbit • NonForagers: pig, poultry
How much to feed? • Depends on function of animal • Pregnant, Lactating, Working, Growing • How often to feed Depends on stomach size & rate of metabolism Stomach size is relavant to amount of feed fed Mink = 4-6 times/day, Cows = 1-2 /day
What foods give energy? • Carbohydrates (starch & cellulose) & Fats • Fat = 2 1/2 times energy of CHO • Energy is major part of a feed ration • Up to 90% of a ration for a steer • Measured in Kilocalories or TDN (Total Digestible Nutrients)
What are Proteins? • Used to build muscle, body tissue • Made of amino acids • Ruminants can make some proteins • Simple Stomachs need specific amino acids
What are Minerals? • Natural elements which regulate certain body functions • Na, Ca, P, Fe, Cu, K, Mn, Mg, Zn, Mo, Se, I, Co • Most are trace minerals
What are vitamins? • Compounds responsible for certain functions • Fat Soluable = A, D, E, K • Water Soluable = B, C
What are additives? • Antibiotics: disease prevention • Coccidiostats: control parasites • Xanthophyll: makes egg yolks yellow • Hormones: increase growth • Tranquilizers: calm nerves (cattle, turkeys) • Antioxidants: prevent feed from getting rancid • Pellet Binders: keep in pellet form • Flavoring Agents: make taste better
Livestock Feeding • Roughage = high fiber, low energy • Concentrate = low fiber, high energy
How is a ration balanced? • Pearson square: balance a ration using any two ingredients for one nutrient • How much Soybean Meal (44% Protein) should be mixed with Barley (13% Protein) to get a mixture that is 16% protein?
Pearson Square • Soybean Meal = 3 parts • Barley = 28 parts • Total Parts = 31 • Soybean Meal = 3/31 or 10% • Barley = 28/31 or 90% • If mixing a ton (2000#) SBM = 200#, Barley = 1800#