Bellringer : Complete the Punnett Square
310 likes | 2.6k Vues
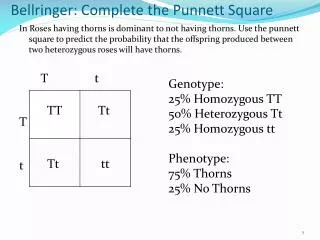
Bellringer : Complete the Punnett Square. In Roses having thorns is dominant to not having thorns. Use the punnett square to predict the probability that the offspring produced between two heterozygous roses will have thorns. T t T t. Genotype: 25% Homozygous TT

Bellringer : Complete the Punnett Square
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Bellringer: Complete the Punnett Square In Roses having thorns is dominant to not having thorns. Use the punnett square to predict the probability that the offspring produced between two heterozygous roses will have thorns. T t T t Genotype: 25% Homozygous TT 50% Heterozygous Tt 25% Homozygous tt Phenotype: 75% Thorns 25% No Thorns TT Tt Tt tt
Bellringer: Complete the Punnett Square Genotype: 50% Homozygous RR 50% Heterozygous Rr Phenotype: 100% Red Flowers • R- Red flowers • r- white flowers R R R r RR RR Rr Rr
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction -REVIEW: What is Heredity? The passing of traits from parents to the offspring. -MAKE CONNECTIONS: How is heredity related to reproduction? Parents create offspring through reproduction which enables them to pass their traits to the next generations.
Sexual Reproduction 1. 2 parents: Male and Female 2. Gametes are created through Meiosis: sperm (male)and egg(female) 3. Sperm and egg join= fertilization. After fertilization occurs the fertilized egg develops into the offspring. 4. Offspring look different from parent (mixed DNA) Sexual Reproduction
Sexual Reproduction • Meiosis- process of cell division that creates reproductive cells (gametes)with ½ the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
Sexual Reproduction • All the members of the Animal Kingdom • Fish • Mammals • Amphibians • Birds • Reptiles • Insects • Crustaceans
Sexual Reproduction • Plant Kingdom • Flowers are the reproductive organs of plants. • Some flowers have both male and female reproductive organs on the same flower. Male flower Female flower
Asexual Reproduction 1. One parent 2. No gametes/reproductive cells are involved 3. Offspring produced by cell division (Mitosis) 4. Offspring identical to parent (same DNA) 5. Several different types of asexual reproduction. Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction • Offspring have 100% the same chromosomes as the parent.
Asexual Reproduction • Binary Fission • Bacteria • Protists Binary fission is a form of asexual reproduction where every organelle is copied and the organism divides in two.
Plant Reproduction • Plant cuttings (Plantlets) Small pieces of a plant are cut off and rooted, to produce a new identical plant.
Tubers:an underground stem that contains stored nutrients (starch). Potatoes can be cut into pieces with each piece having an “eye” which can grow into a new potato plant. Plant Reproduction
Bulbs: Short underground stems surrounded by thick fleshy leaves that contain stored food. New bulbs sprout from the old one. Each bulb can grow into a new plant Ex. Onions, tulips, garlic. Plant Reproduction
Plant Reproduction • Runner :Stem that grows sideways along the surface of the ground that has buds that can grow into new plants when they contact soil. • Ex. Strawberry plants
Rhizome: Stem that grows sideways underground. Enlarged portions called nodes grow into buds which can form new plants. Ex. Irises, ginger. Plant Reproduction
Budding • Yeast • Hydra Budding is a means of asexual reproduction where a new individual develops from an outgrowth of a parent, splits off, and lives independently.
Regeneration -Starfish Regeneration occurs when a body part has broken off and the organism grows a new one.
Regeneration Leech • Fragmentation Fragmentation is a means of asexual reproduction where a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.
Sporulation: Spore formation • Occurs in fungus, algae and mold • Tiny spores form inside the parent cell and are released and can grow into an adult organism.
Homework:Make a Venn Diagram Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Both Types of reproduction in living organisms Pass DNA from parent to offspring