Evolution of Learning in Songbirds: Brain Nuclei, Cognitive Abilities, and Sexual Selection
180 likes | 305 Vues
Explore how brain nuclei size influences song learning in songbirds, impacting cognitive abilities and sexual selection through feeding efficiency and early experiences.

Evolution of Learning in Songbirds: Brain Nuclei, Cognitive Abilities, and Sexual Selection
E N D
Presentation Transcript
(b) Instrumental conditioning (a) Classical conditioning Stimulus absence (SD) Static features (CS) Aversive internal state Movement or other salient feature (US) Following response (Ri) Recognition (UR) Aversive internal state is reduced (SR) Following response Following response strengthened 12.3
(b) (a) Lesioned birds 12.4
Isolation 12.6
Hobbyhorse-reared monkeys Dog-reared monkeys Catfish Fonsie Ron KC Shawn Sandy Poppy Marcy Tasha Sue Ping Jarvis Proximity Agonistic Affiliative 12.10
Porifera (sponges) Myxinoidea (hagfishes) Cnidaria (jelly fish, coral) Petromyzontidae (lampreys) Ctenophora (comb jellies) Chondrichthyes (sharks) Nematoda (round worms) Actinopterygii (bony fish) Rotifera (rotifers) Echinodermata (sea urchins) Latimeria (coelacanths) Bryozoa (bryozoans) Dipnoi (lungfishes) Brachiopoda (lamp shells) Amphibia (frogs) Phoronida (rube worms) Chelonia (turtles) Chordata (vertebrates) Aves (birds) Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Nemertea (ribbon worms) Crocodylia (crocodiles) Mollusca (octopuses) Lepidosauria (lizards) Annelida (earthworms) Arachnida (spiders) Prototheria (platypus) Crustacea (lobsters) Metatheria (kangaroos) Myriapoda (centipedes) Insecta (ants) Eutheria (placentals) 12.12
10 (a) 5 0 10 (b) Frequency (kHz) 5 0 10 (c) 5 0 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Time (s) 12.13
Swamp Sparrow Song Sparrow Normal song Isolate song: Hearing intact Isolate song: Deafened before singing 12.14
Adult life Sensorimotor learning phase • Crystallized or adult song • Plastic song • Subsong First breeding season (spring) Juvenile period (fall and winter) Sensory learning phase • No song production • Acquisition of an auditory memory • Flexible sensitive period • Initial social interactions • Exposure to song Nesting period Hatching (summer) 12.15
San Francisco Bay Area Morin 5 kHz 0.5 s Berkeley Sunset Beach 12.16
Anterior telencephalon DLM Area X LMAN Posterior telencephalon NO HVC RA Cochlear nucleus Nucleus of the Hypoglossal nerve N. VIII N. XII Basilar membrane Syringeal muscles Song (input) Vocal behavior (output) 12.17
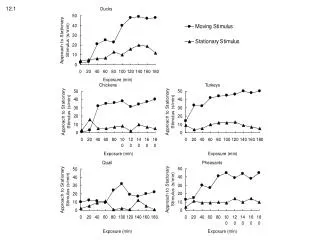
Size of brain nuclei involved in song learning Quality of song repertoire (a proxy for cognitive abilities related to foraging efficiency) Endocannabinoid brain levels Female sexual preference Early nutrition Early stress Feeding efficiency during the plastic song phase Sexual selection contributing to the evolution of a large telencephalon and higher cognition in songbirds 12.18