Script Formats
170 likes | 334 Vues
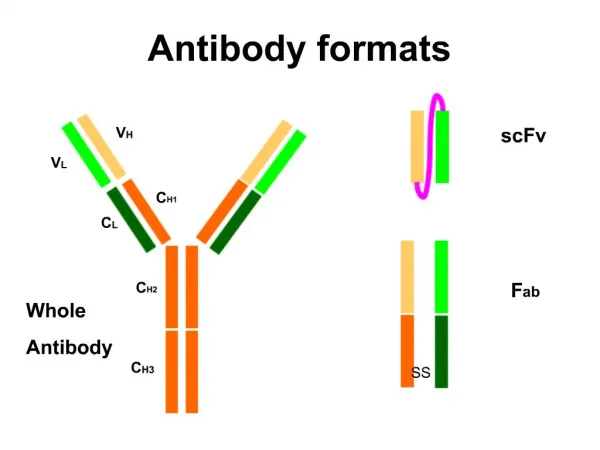
Script Formats. Format. There are different kinds and vary for both television, radio and film. There is the single column format:. Radio: Script “Americans at Work” 1939. Then there is . The two column format. Typically used for Television. . Proper Format .

Script Formats
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Format • There are different kinds and vary for both television, radio and film. • There is the single column format:
Then there is • The two column format. • Typically used for Television.
Proper Format • Essential so you don’t look like an amateur. • Common mistakes are typos, punctuation errors and poor grammar • When writing a script – Keep it simple. • They should be three hole punched. • Card stock paper in a single color. • Don’t write with fancy typography. Use courier 12 or Times New Roman.
For Screenplays • Titles: Should be in all CAPS and centered, about a 1/3 of the way down the page. • Can be plain underlined or in quotation marks but not both. • Should have you name centered and double spaced below the title. Not all in caps. • Your contact info • Font should be courier 12, New York, Bookman and Times New Roman.
Ways to format a script for TV/radio • The single column – the way most screenplays are written. This is also used in radio.
Summary • For a commercial idea the summary or outline might be a few sentences with the scenario or treatment ranging from a paragraph to a page. • For movies or a 1-hour drama it can be a summary of 1 to 2 pages and the treatment can be a 5th of the entire projected script.
Style… • For broadcast – be brief as you are constrained by time. • 25 to 30 words is equivalent to about 10 seconds. • Retain an informal tone. • Be specific. Do Not generalize or confuse the audience. • Use of Gender: Don’t assume the use of “he” or “his.” Try to generalize and include both sexes.
Radio Style • Writing is more “one on one” • Material must be written as if the presenter is sitting in the audiences living room. • Personalize: Reach out to a specific audience. Try to relate. • Be natural. • Choose words that are familiar (also for TV).
Grammar • Slang words can be used in certain circumstances. • Mostly use common language. • Spelling must be accurate – esp. for a newscast. • Verbs: Must be in present tense to an active voice with subjects doing the action.
The right words: • Know their meaning and their spelling. • Affect v.s. effect • Advice v.s. advise • It’s and its • Your and you’re • Punctuation – gives the narrator or actor direction about the tone. Avoid abbreviations except for terms that can’t be misunderstood like Mr., Mrs., Dr., etc.
Pronunciation • Must be clear • If you have a word that is pronounced different than how it is spelling place pronunciation in all caps next to it. • Ex: We go live to Sandra Hinojos (EE-NO-HOSE).
One more thing – Be Accurate • When doing your own commercial – do your own outside research. • If you claim that your product is the first of its kind in the history of products - then you will need the proof to back it up. • You don’t want to be sued for False Advertising or making False Claims. • Recent Examples – Kelloggs must pay $4 million for falsely advertising mini-wheats. • Sketcher’s Shoes case - $40 million settlement.
ASSIGNMENTS • Read chapter 3 of Hillard • Due Wednesday: Select an online or television commercial, trailer, PSA, or broadcast piece and using the two column writing style write its script. • Example: Pages 54 and 55 of Hillard.