Precambrian Eukaryotes
940 likes | 1.24k Vues
Precambrian Eukaryotes. Acritarchs Ediacaran Vendian. Cysts of unicellular eukaroytes, perhaps algae or egg cases of multicellular orgs. 1800 my through Devonian. Acritarchs. Ediacaran. 600 my-545 my Soft-bodied Many organisms of uncertain affinity.

Precambrian Eukaryotes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Precambrian Eukaryotes Acritarchs Ediacaran Vendian
Cysts of unicellular eukaroytes, perhaps algae or egg cases of multicellular orgs. 1800 my through Devonian Acritarchs
Ediacaran • 600 my-545 my • Soft-bodied • Many organisms of uncertain affinity
Possible mollusc? Probable cnidarian
Vendian • “little shellies” • Right at Cambrian boundary
Phanerozoic Life, Part I. • Cambrian, Paleozoic and Modern Faunas slides • Phanerozoic Aquarium project: with your partners, go through your Aquarium pages. Identify each organism using your handouts: Invertebrates, Fish, Tetrapods • Time Travel Submarine
Cambrian Trilobites: Extinct arthropods (like lobsters or shrimp but with calcite skeleton)
Burgess Shale • Middle Cambrian • Excellent preservation of soft-bodied orgs. • 5 kinds of arthropods (only 3 kinds today) • First vertebrate • Mysterious critters
Cambrian • Smallish • Skeletons (if any) of phosphate or thin CaCO3 • Live on or near ocean floor • Sponges, trilobites, early molluscs, echinoderms, lingulate brachiopods
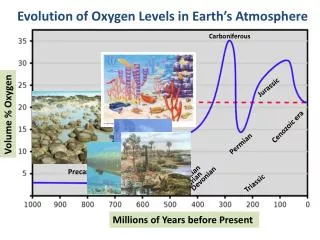
Why the Cambrian explosion in diversity? • Proterozoic glaciation • Atmospheric oxygen • Proterozoic rifting • Changes in ocean nutrients • Extinction of cyanobacteria • Evolution of predators
Ordovician Brachiopods (articulate)
Ordovician invertebrates • More robust skeletons • Calcite skeletons • Taller, deeper (take up more ecological space) • The Paleozoic fauna appears: rhynchenelliform brachiopods, bryozoans, crinoids/blastoids, primitive cephalopods, graptolites, rugose/tabulate corals
Middle-Late Paleozoic • Increasing height, increasing depth • Increasing diversity • New organisms • Eurypterids (giant sea scorpions) • Fish/amphibians
Oceans - a whole new crew The Modern Fauna Mollusks Crustaceans Echinoids Fish Mesozoic Life
Bivalves Molluscs Gastropods
Oceans - a whole new crew The Modern Fauna Mollusks Crustaceans Echinoids Fish Plus marine reptiles and ammonites Mesozoic Life
Cenozoic Oceans • Like Mesozoic: Modern Fauna • Minus marine reptiles and ammonites • Plus whales and marine mammals
Phanerozoic Life, Pt. II • Find your Phanerozoic Terrarium pages. • As we go through the Powerpoint slides, find organisms in the appropriate time period. • Safari Through Time • Extinction
Evolution of Tetrapods • Arise from sarcopterygians (lobe-finned fish) • Amphibianish creatures • Reptiles (to birds) • Mammals
Adaptations for life on land • Breathe! • Locomotion • Avoid dessication • Reproduction - amniotic egg allows longer development (no swimming larvae) • Leathery covering or eggshell • Larger size of egg • Larger yolk
Adaptations for life on land: plants • Avoid dessication – thicker outsides • Reproduction – • Fancy fertilization methods, seeds • Marine plants release gametes into water • More complicated dispersal mechanisms for young
Reptiles • Anapsids: turtles and their ancestors • Synapsids: pre-mammals & mammals