Iowa in Motion
220 likes | 349 Vues
Iowa's transportation plan is structured through a phased approach focusing on current conditions, alternatives development, and implementation strategies. The analysis covers issues within Iowa's transportation infrastructure, such as highways, bridges, and rural access. It emphasizes the state's changing needs driven by population growth, economic focus, and urban development. The plan summarizes accomplishments from 1995 to 2020, highlighting significant investments in preserving and improving mileages, enhancing safety measures, and utilizing resources effectively for sustainable transportation development.

Iowa in Motion
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Iowa in Motion • Iowa’s Plan Process • Phased Approach • Part 1 - current conditions - issues - elements
Part 11 - alternatives development - analysis/review • Part 111 - alternatives selection:draft plan - final state transportation plan approval • Part 1V - implementation plans development
Iowa’s Changing Transportation Needs • Population • Employment • Travel
Primary Highway System • Interstates • CIN • Area development routes • Access routes • Local service
Investment Alternatives • Benchmark • Reduced spending • Resource conservation • Expansion/development • Economic/urban focus • Rural focus
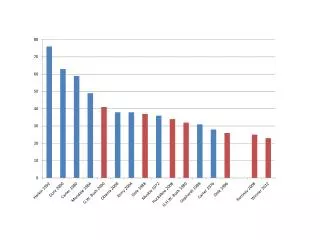
Summary of Interstate Accomplishments by the year 2020 • Preserve 252 miles • Rebuild 458 miles • Capacity/operational improvements-71miles • Repair or replace 1,000 bridges and culverts 1995 2020 • Sufficiency Rating 88 85 • Vehicle Miles of Travel 5,790 9,384 (millions)
Summary of Interstate Accomplishments by the year 2020 • Preserve 483 miles • Rebuid 113 miles • Capacity improvements Four-lane 566 miles Super-2 969 miles • New location improvements - 376 miles • Repair or replace 2,000 bridges and culverts • Eliminate narrow roadways - 39 miles • Evaluate 34 rail/highway at-grade crossings 1995 2020 • Sufficiency Rating 64 80 • Vehicle Miles of Travel 4,219 7,458 (millions)
Summary of other primary Highway Accomplishments by the year 2020 • Preserve 3,678 miles • Rebuid 1,157 miles • Capacity improvements Four-lane 70 miles Super-2 80 miles • New location improvements - 31 miles • Repair or replace 3,750 bridges and culverts • Eliminate narrow roadways - 39 miles • Evaluate narrow roadways - 1,871 miles 1995 2020 • Sufficiency Rating 64 63 • Vehicle Miles of Travel 6,201 8,794 (millions)
Iowa in Motion Average1996-2020Approximate Perentage of Plan Costs by System
Investment SummaryHighway/BridgesAverage Investment/Mile/Year
Investment SummaryHighway/BridgesMiles with no-Improvement over 25 Years Priority on higher level systems
Recommended Improvement Investment GuidelinesApproximate Percentage of Available funding by Improvement Category
Annual Iowa DOT Highway Program ($ in millions) Federal includes obligation limits no special projects State RUTF $409 $141 Maintenance Operations U-STEP, C-STEP Rail Crossing Contracts Maintenance Bridge Painting $550 $234 Minus Formula funds available for construction work $316 ISTEA Does not include special projects ISTEA - 92.5%, TEA-21 - 88%obligation
Annual Iowa DOT Highway Program ($ in millions) Federal includes obligation limits no special projects State RUTF $409 $475 $141 $194 $550 $669 Maintenance Operations U-STEP, C-STEP Rail Crossing Contracts Maintenance Bridge Painting $234 $272 Minus Formula funds available for construction work $316/$397 ISTEA/TEA21 Does not include special projects ISTEA - 92.5%, TEA-21 - 88%obligation
Planning and Project Development Replaces the 16 metropolitan and 23 statewide planning factors with seven broad factors or strategies which will: • support economic vitality; • increase safety; • increase accessibility and mobility; • protect and enhance the environment;
Planning and Project Development • enhance the connectivity and integration between modes; • promote efficient system management and operation; and • emphasize the preservation of the existing system.
Planning and Project Development Metric Conversion • Removed a requirement that federal-aid highway projects use the metric system.
Research and Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) • $603 million for research, training and standards development. • $482 million for acceleration of integration and inter-operability, metro and rural. • $184 million for deployment of commercial vehicle ITS.
Highway Safety Programs • Two programs were established which impose sanctions on states to encourage states to enact state laws dealing with: • open alcohol containers in vehicles and • penalties for repeat OWI offenders.
Highway Safety Programs • Three incentive programs were established which provide additional funding for states to encourage: • increased seat belt usage in the state, • enactment of a law that provides for a .08 percent BAC drunk driving standard, and • improvement to highway safety data collection and accessibility.