Working Memory Deficits & Learning
370 likes | 1.19k Vues
Working Memory Deficits & Learning. Interventions Amy Williams EDPS 658. Presentation Overview. Definition of Working Memory Short-Term Memory Vs. Working Memory Baddeley’s Model of Working Memory Working Memory and Learning Working Memory Deficits and Learning LDs

Working Memory Deficits & Learning
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Working Memory Deficits & Learning Interventions Amy Williams EDPS 658
Presentation Overview • Definition of Working Memory • Short-Term Memory Vs. Working Memory • Baddeley’s Model of Working Memory • Working Memory and Learning • Working Memory Deficits and Learning LDs • Working Memory Deficits: Impact on Learning • Warning Signs • Interventions • Classroom Instruction • Reading • Math • Writing • Metamemory Awareness & Training • Conclusion
Definition of Working Memory “Working memory is a limited capacity store for retaining information for a brief period while performing mental operations on that information.” (Miller, 2007, p. 201)
Working Memory vs. Short-Term Memory 283019 910382
Working Memory vs. Short-Term Memory Dehn, M. J. (2008). Working Memory and Academic Learning: Assessment and Intervention [Kindle version]. D01-7449388-8845746
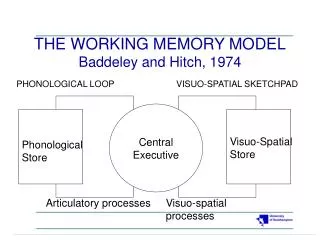
Baddeley’s Model of Working Memory Control Centre Phonological Loop Central Executive Visuospatial Sketchpad Verbal Working Memory Non-verbal Working Memory (Baddeley & Hitch,1974; Dehn, 2008; Miller, 2007)
Working Memory & Learning • “a primary function of working memory is to facilitate learning” (Dehn, 2008, Chapter 9, “Effective Teaching Practices”, para. 11) • Working memory is involved in all academic areas • Reading • Math • Writing • Important in school years and beyond
Working Memory & Learning Working Memory Components Most Highly Related to Types of Academic Learning Adapted from Working Memory and Academic Learning: Assessment and Intervention (Chapter 5, “Working Memory and Learning Disabilities”), by M. J. Dehn, 2008, [Kindle version]. D01-7449388-8845746
Working Memory Deficits & LDs • Deficits in Working Memory do not cause LDs • LDs in domain-specific areas are associated with deficits in related working memory components • Working Memory deficits often coexist with other cognitive deficits • Capacity deficit versus strategy deficit (Swanson, 2000)
Working Memory Deficits: Impact on Learning • Difficulty meeting working memory demands of learning situations • Overloaded working memory • Task abandonment or giving up • Lack of motivation • Missed learning opportunities • Learning delays
Warning Signs • Incomplete recall/ “I forgot” • Difficulty following instructions • Place-keeping errors • Task abandonment • Skipping or repeating words when writing • Inattention • Inability to monitor the quality of work Gathercole, S.E., & Packiam Alloway, T. (2008). Working Memory and Learning: A Practical Guide for Teachers [Kindle version]. D01-6315489-9831300
Classroom Instruction • Direct instruction • Repetition of instructions • Shorter, simpler instructions that can be broken down into individual steps • Time for rehearsal and processing • Providing a quiet environment • Memory or visual aides - training • Encouraging child to ask for help
Decoding Use of Pictures Chunking Self-Monitoring Comprehension Monitoring (Stop & Check) Rereading the Text Visualization Previewing strategies Help activate prior knowledge Guided practice Paraphrasing Time Interventions for Reading
Interventions for Math • Basic Skills • 3-D manipulatives (cubes and blocks) • Number lines • Multiplication grids • Calculators • Memory cards with vocabulary or formulae Problem-Solving • Pictures • Irrelevant vs. relevant information • Graphic organizers
Interventions for Writing • Idea Generation • Sentence starters • Choice • Pictures/objects/visuals • Prewriting and graphic organizers • Emphasis on the Writing Process • Word processing programs • Using a scribe • Note-Taking • Audio recording devices for writing notes • Use of teacher’s notes
Interventions for Writing • Spelling • Flashcards • Word Walls • Personalized word lists • Key vocabulary written on board • Word processing programs • Spelling rules in the form of rhymes (‘i’ before ‘e’ except after ‘c’)
Metamemory Awareness & Training • “metacognition as it applies to memory” (Dehn, 2008, Chapter 9, “Metamemory Training”, para. 1) • Self-awareness and education • Explanation of working memory and how it works • Emphasis on working memory overload • Memory strategies & training • Self-advocacy
Conclusion • Effective Working Memory Interventions: • Are compensatory • Reduce demand on child’s working memory, thus preventing overload • Involve repetition of information (and patience!) • Involve the use of visual and external memory aids • Require training and practice • Foster confidence and independence • Enhance overall learning
References • Baddeley, A., & Hitch, G. (1974). Working memory. In G. H. Bower (Ed.), The psychology of learning and motivation (Vol. 8, pp. 47-89). New York: Academic Press. • Dehn, M. J. (2008). Working Memory and Academic Learning: Assessment and Intervention [Kindle version]. D01-7449388-8845746. • Gathercole, S.E., & Packiam Alloway, T. (2008). Working Memory and Learning: A Practical Guide for Teachers [Kindle version]. D01- 6315489-9831300. • Miller, D. (2007). Essentials of School Neuropsychological Assessment. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons. • Sattler, J.M. (2008). Assessment of Children: Cognitive Foundations (5th Edition). San Diego, CA: J. Sattler. • Swanson, H. L. (2000). Are working memory deficits in readers with learning disabilities hard to change? Journal of Learning Disabilities, 33, 551- 566 • Wendling, B. and Mather, N., (2009). Essentials of Evidence-Based • Academic Interventions. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons.