FIBROID UTERUS
550 likes | 887 Vues
FIBROID UTERUS. Introduction. Fibromyomas / Leiomyoma/ fibroids/myomas Benign neoplasm 5-20% in reproductive age Derived from smooth muscle cell rests either from vessel wall and uterine musculature. AETIOLOGY. Common in NP Increased familial incidence, 1 st degree relatives 2.5 times

FIBROID UTERUS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Introduction Fibromyomas / Leiomyoma/ fibroids/myomas • Benign neoplasm • 5-20% in reproductive age • Derived from smooth muscle cell rests either from vessel wall and uterine musculature.
AETIOLOGY • Common in NP • Increased familial incidence, 1st degree relatives 2.5 times • Higher incidence in blacks • Chromosomal abnormalities in 40% • Estrogen dependent tumor contains more Estrogen receptors • Role of growth factors • obesity • smoking, exercise -
Introduction • Typical myoma is well circumscribed with a pseudo capsule, firm in consistency. C/S –Pinkish white and has a whorled appearance capsule has CT which fixes tumor to myoma. • Blood vessels lie in capsule and send radial branches into the tumor. • Calcification seen at periphery. M/S –Consists of bundles of plain muscle cells, separated by varying amount of fibroins bands.
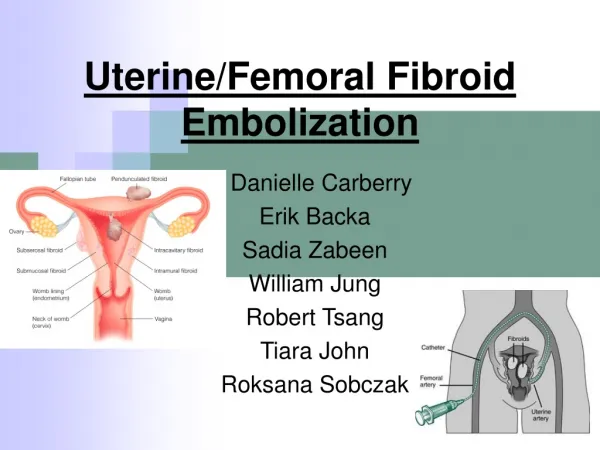
Introduction • Myoma- hyperplasia of myometrial wall. • Cavity is often distorted and enlarged. • Endo tends to be thicker due to end hyperplasia • ovaries are enlarged cystic – hyperemic with evidence of SO – 15%
Classification Uterus • Intramural / interstitial subserous- pendunculated – parasitic • Submucous – pedunculated – polyp cx – commonly single (1-2%) anterior, central, posterior,lateral extrauterine - RL, utero ovarian, uterosacral vagina, vulva • broad ligament fibroids are usually single – true/false
Secondary changes • Atrophy – after menopause, follow delivery and with GnRH Rx • Hyaline • cystic • fatty – usually seen in centre of fibroid. • Calcareous – Womb stones in graveyard • Red degeneration • sarcomatous
Red degeneration/ necrobiosis • Frequently seen during pregnancy / puerperium. • Tense/tender cause severe abdominal pain with constitutional upset , fever , vomiting. Tumor assume a peculiar purple red colour. • Develops a fishy odor • Large vein and small vessels are thrombosed • Discoloration is caused by diffusion of blood pigments from the thrombosed vessels. • Fever, leucocytosis raised ESR • Condition in aseptic • D/D – appenditicitis, twisted ovarian cyst, pyelitis, APH
Sarcomatous change • rare, <0.5% • Intramural/ submucus have a higher potential for SC • Commonly seen in PM women when tumor grows suddenly causing pain, PMB. • To naked eye, a sarcomatous myoma is yellowish grey in colour and Hge, soft and friable. • non encapsulation of tumor. • It is highly malignant spreads via the blood stream.
Other complications of myoma • Torsion • Inversion • Capsular Hge • Infection – submucus / myomatus polyp protruding from Cx canal. • Endo Ca – 3%
Symptoms • Menorrhagia, polymenorrhia, metrorrhagia • Pain – • Infertility – due to ass. PID, endometriosis, an ovulation, obstruction to sperm ascent, poor nidation, cornual block. SM fibroid >4cm responsible for infertility and RPL – 20% • Pressure symptoms • abdominal lump, • vaginal discharge.
Pressure symptoms • Anterior / posterior fibroid – frequency / retension of urine • Broad lig fibroid – hydroureter – hydronephrosis • Constipation • Intestinal obstruction • Ass condition – follicular cysts of ovary endo hyperplasia endo ca, endometriosis
Clinical features • Anemia, palpitation, lassitude • Abdominal lump – arising from pelvis, well defined margins, firm in consistency smooth, bossy surface • polycythaemia, • hypoglycemia (retroperiotoneal)
D/D • Pregnancy : • Hematometra, • Adenomyosis • Endometriosis • Bicornuate • EP • Ch PID • Benign ovarian tumor • Chronic inversion
Investigation • HB • Blood group and Rh type • USG - Site, size, NO,ET follow up of fibroid after menopause while following Gn RH therapy • HSG – Identifies a submucus fibroid, patency • Saline salpingography • Hysteroscopy • D/C
Management • Asymptomatic fibroid – observed every 6 months • Indication for treatment in an asymptomatic fibroid. • Infertility – corneal fibroid, submucous fibroid • Fibroid >12 weeks & penduculated fibroid • Fibroid causing pressure on ureter • Rapidly growing fibroid in PM
Medical therapy • Purpose is to control menorrhagia • Improve Hb before surgery • To shrink the fibroid • In older women will allow to reach menopause
Drugs • RU 486 / Mifepristone 10-25mg. Daily x 3 months • Low dose OCP • Gestrinon 2.5 thrice weekly • Asoprisnil • GnRH – used for 6 months • Reduction in size by 50-80% • Reduces vasularity • Restores Hb • Allows Pfannenstiel incision • Convert into vaginal hysterectomy • Monthly depot inj. 3.6mg IM Disadvantages : makes enucleation difficult small fibroids become invisible
Surgery Minimal – Uterine artery embolization MRI guided laser ablation. lap myolysis • Myomectomy vaginal myomectomy hysteroscopic myomectomy laparoscopic laparotomy • hysterectomy : vaginal/abdominal/LAVH/ laparoscopic
Myomectomy • Indicated in infertile woman. • Woman desirous of child bearing • wishes to retain uterus.
Prerequisite • May be difficult – hence hysterectomy consent • Semen analysis of partner • exclude Ca endo • Arrange adequate blood • Pap smear • On opening examine the adnexa b/l tubal blocks will change the decision • Midline/ vertical incision for ant/post wall fibroids
Hge- myomectomy clamp, vasopressin, tornique • Large cavities by mattress sutures or baseball sutures • Preg rate 40-50%, • 10-15% develop menorrhagia • Recurrence rate of leiomyoma after myomectomy is 5-10%
myomectomy Vaginal myomectomy : Submucus fibroid polyp. • Hysteroscopic myomectomy : Submucus fibroid- Removed cautery, laser, resectoscope • Laparoscopic myomectomy : Penduculated fibroid. Subserous fibroid not exceeding 10cm in size, not >than 4 in No.
Complications : • Primary, reactional/secondary Hge • Trauma to bladder, bowel, infection • Adhesion intestinal obstruction • Recurrence
Hysterectomy Routes : • Abdominal • Vaginal • Laparoscopic - C/I – uterus size >14 weeks Broad lig Cx fibroids • LAVH
Complications of Hysterectomy • Primary, reactionary, secondary Hge. • Trauma to bladder, ureter, bowel. rectum • Anesthetic complication • Paralytic illus, intestinal obstruction • Pulmonary embolism • Chest infection • Burst abdomen, scar, hernia • Post-op infection – wound, peritonitis,DVT
Late complication • Abdominal adhesions – ch. Abdomen pain • Residual ovarian syndrome • Dyspareunia • Chronic pelvic pain • Surgical menopause • Vault prolapse • Ovarian cancer
Uterine artery embolization : (UAE) • First of performed in 1991 • Reduces menorrhagia in 80-90% • Pressure symptoms in 40-70% • Volume by 50%
Contra indication • Subserous and penduclulated, fibroids, • big fibroid, • Sub mucus fibroid • Those who are infertile • active genital infection, • diminished immune status • impaired RFT, • vascular disease.
Procedure • Under local sedation, Bil. uterine artery are approached thro’ percutaneous femoral catheterization, using PVA gel foam particles or metal coils, trisacryl gelatin • Causes avscular necrosis
Post-op. complications • Fever and infection • Vaginal discharge/bleeding • Ischemic pain • Pulmonary embolism • Ovarian failure – accidental ovarian vessel blockage • Fertility is reduced.
MRI guided percutaneous laser ablation using high intensity focused US (HIFU) low morbidity/rapid recovery. • Laparoscopic myolysis – Nd: YAG laser, cryoprobe
Fibroid complicating pregnancy • Prevalence of fibroid among pregnant women is 18% in African, American 8% white • Effect preg. on fibroids – • do not increase in size, • degeneration during preg.
Effect of fibroid on preg abortion PTL PROM, chorioamnionitis operative vag del PPH rupture of scar