Control of gene expression
650 likes | 1.12k Vues
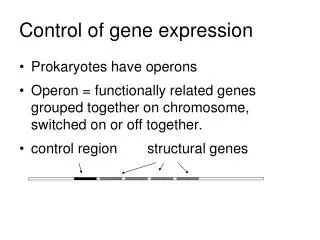
Control of gene expression. Transcriptional Post-transcriptional Epigenetics and long range control. Control of gene expression. Transcriptional Tissue specific transcription factors Binding of hormones, growth factors etc. to response elements

Control of gene expression
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Control of gene expression • Transcriptional • Post-transcriptional • Epigenetics and long range control
Control of gene expression • Transcriptional • Tissue specific transcription factors • Binding of hormones, growth factors etc. to response elements • Use of alternative promoters in a single gene
Control of gene expression • Post-transcriptional • Alternative splicing • Alternative polyadenylation • Tissue specific RNA editing • Translational control mechanisms
Control of gene expression • Epigenetics and chromatin structure • Allelic exclusion (rearrangements, imprinting, X inactivation) • Long range control by chromatin structure (position effects Pax6 in aniridia) • Cell position-dependent, short range signaling
Control of gene expression • rRNA synthesis • Arrows indicate cleavage sites
Control of gene expression • Initiation of transcription (RNA pol I)
Control of gene expression • tRNA and 5s RNA promoter elements • Initiation of transcription (RNA pol III)
Control of gene expression • Conserved locations of promoter elements in eukaryotes
Control of gene expression • Insulin gene promoter organization • NRE negative regulatory element • CRE cAMP response element
Control of gene expression • HS-40 alpha-globin regulatory site • Tissue specific regulation (many sites)
Control of gene expression • Structural domains in transcription factors • HTH • HLH • Zn Finger • Alpha-helix
Control of gene expression • Binding of conserved motifs to double helix
Control of gene expression • Steroid receptors and response elements • GR • ER • PR • RAR • TR • VDR
Control of gene expression • Transcription regulation by glucocorticoids
Control of gene expression • Target gene expression via signal transduction • Protein kinase: hormonal signaling through cAMP-pt kinase A pathway • Cytoplasmic transcription factor NF kappa B and translocation to the nucleus
Control of gene expression • Major Classes of Cell Surface Receptor • G protein coupled • Serine-Threonine kinase • Tyrosine kinase • Tyrosine kinase associated JAK (janus protein kinase) activity in JAK-STAT signaling • Ion channel-linked
Control of gene expression • Secondary Messengers in Cell Signaling • Cyclic AMP (cAMP) • Cyclic GMP (cGMP) • Phospholipids/Ca
Control of gene expression • The IRE binding protein and iron-response elements (IREs)
Control of gene expression • Genes with multiple promoters • Dystrophin has eight promoters
Control of gene expression • Differential RNA splicing • Wt1 Wilm’s tumor (four splice forms) • Calcitonin gene (tissue specific products)
Control of gene expression • Tissue specific RNA editing • Apolipoprotein B gene (rare)
Control of gene expression • Methylation and gene expression • Largely confined to CpG dinucleotides • CpG islands • Methylation patterns change during development • Sex-specific regulation
Control of gene expression • Methylation • CpG islands
Control of gene expression • Methylation • Changes in methylation throughout development
Control of gene expression • Methylation • Sex-specific regulation of the Dnmt1 methyl transferase gene • 1so somatic • 1sp spermatocytes • 1oo oocytes
Control of gene expression • Transcriptional repression by histone deacetylation • Mediated by methylation • Methylated CpG’s bound by MeCP2 repressor