Module 56
160 likes | 297 Vues
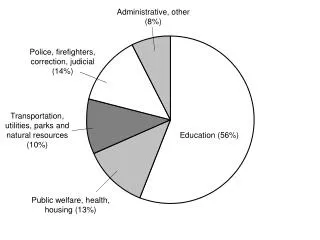
Module 56. Conformity Studies. Adjusting one’s behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard. Asch’s Study of Conformity. Asch’s Results. About 1/3 of the participants conformed. 70% conformed at least once. To strengthen conformity: The group is unanimous

Module 56
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Conformity Studies • Adjusting one’s behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard.
Asch’s Results • About 1/3 of the participants conformed. • 70% conformed at least once. To strengthen conformity: • The group is unanimous • The group is at least three people. • One admires the group’s status • One had made no prior commitment
Milgram’s Study Of Obedience
What did we learn from Milgram? • Ordinary people can do shocking things. • Ethical issues…. • Would not have received approval from today’s IRB (Internal Review Board).
What did we learn from Milgram? • Why were people more likely to obey? • When the person giving orders were nearby and was perceived as a legitimate authority figure. • The person giving the order was supported by a prestigious institution • the victim was depersonalized
Group Influence • Social Facilitation: stronger responses on simple or well learned tasks in the presence of others(better performance) • The more difficult the task people perform less well. (complex multiplication).
Social Loafing • The tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward attaining a common goal than when individually accountable. • Why? • Less accountable • Laziness is contagious • Contribution is not important
Deindividuation • The Misconception: People who riot and loot are scum who were just looking for an excuse to steal and be violent. • The Truth: You are prone to losing your individuality and becoming absorbed into a mob under the right conditions
Group Polarization • Groups tend to make more extreme decisions than the individual.
Group Think • The mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision making group over rides a realistic appraisal of alternatives. • Why? Overconfidence, conformity, self justification, & group polarization
Symptoms of Groupthink • Illusions of invulnerability • Collective rationalization and discounting of warnings • Unquestioned belief in the group’s inherent morality • Stereotyped views of the enemy • Direct pressure on any group member who argues against the group’s stereotypes, illusions, or proposals • Self-censorship of disagreement with the group’s apparent consensus • Shared illusions of unanimity • Self-appointed mindguards who protect the group from adverse information that might shatter their complacency SOURCE: Janis,Victims of Groupthink
Conclusion: debate and buy-in “I don’t care how smart you are….Success and failure depends on how well the staff and cabinet debate honestly and openly and then unite once you’ve made a decision.” Bill Clinton Diversity in counsel, unity in command. - Cyrus the Great