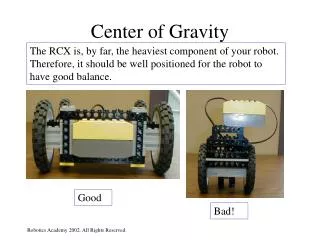
Center of Gravity
30 likes | 213 Vues
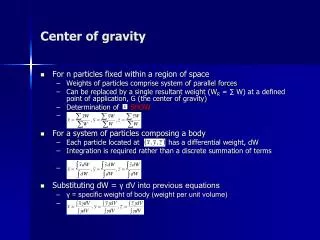
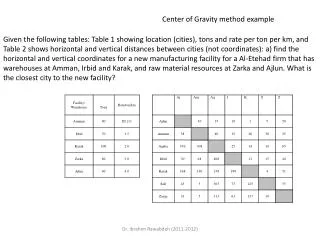
Center of Gravity. H. CG. CG. CG of sphere is its geometric center. 1/3 rd H. CG. 10 kg. 10 kg. CG. 5 + 10 = 15 kg. 10 + 5 = 15 kg. CG. CG. 2 + 10 = 12 kg. 10 + 8 = 18 kg.

Center of Gravity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Center of Gravity H CG CG CG of sphere is its geometric center 1/3rd H CG 10 kg 10 kg CG 5 + 10 = 15 kg 10 + 5 = 15 kg CG CG 2 + 10 = 12 kg 10 + 8 = 18 kg The center of gravity is the average location of weight of an object. It is the point from where the whole weight of the object seems to act Every object that has mass has a center of gravity. Where the CG is depends on the geometric property of the object, primarily its shape. In a regular geometric solid with uniform density, the center of gravity is the object's geometric center. CG point does not depend on how much mass an object has, instead it depends on how the mass is distributed. Example - Here the mass distribution is uniform. The rod has equal weights on both sides. CG is at the center. Even though the total mass has increased, the distribution of mass is still the same. We have equal weights of 15 kg on both ends of the rod. The CG is still at the geometrical center. The total mass is still the same (30 kg). But the distribution of mass has changed. The position of CG has shifted. It has moved closer to the heavier side. Another important concept :: The CG point need not always lie on the object. It could be outside the object. This is for the same reason that CG depends more on the mass distribution than on the mass itself. CG is at the center of the ring, where there is nothing to support it. Balancing an object is easier if you support it along the center of gravity. To keep an object in balance for a long time you have to support it at the exact CG or at any point along a line passing through the CG. Least effort is required if you are trying to balance a heavy object this way.