Efficient Rapidzone Operations for Optimal Network Data Sharing and Zone Control
70 likes | 202 Vues
This document outlines the operational mechanics of Rapidzone systems, focusing on the dynamic data sharing of air temperature information to zone controllers via E-Bus. It details how the zone controller dictates the deadband for heating and cooling via a setpoint knob, illustrating with an example. Furthermore, it discusses the terminal load operations, emphasizing how deviations from setpoints trigger the heating or cooling responses in various zones and the configuration priorities for effective temperature management.

Efficient Rapidzone Operations for Optimal Network Data Sharing and Zone Control
E N D
Presentation Transcript
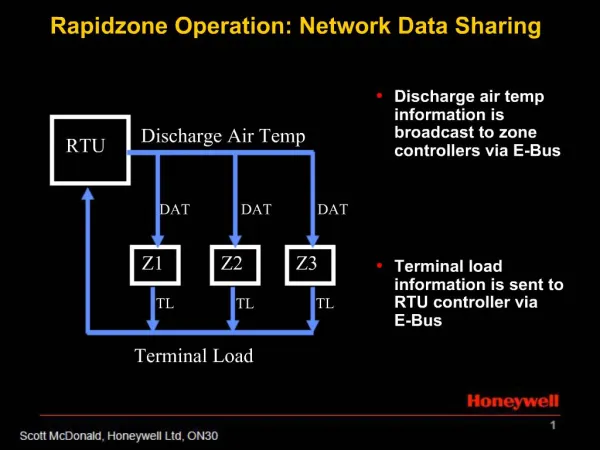
1. Rapidzone Operation: Network Data Sharing Discharge air temp information is broadcast to zone controllers via E-Bus
2. Zone Controller Operation: DAT Control
3. Setpoint Knob Operation Setpoint knob determines centre of deadband between heating and cooling
Example:
deadband is set for 6�
knob set for 73�
heat setpoint becomes 70 �
cool setpoint becomes 76 �
deadband exists between 70 � - 76 �
4. Rapidzone Operation: Terminal Loads Terminal Load: zone deviation from setpoint
Terminal Load is broadcast from each zone to RTU via E-Bus
< 20 % zone is satisfied
> 20 % zone requires heating or cooling
Zones can be configured as �priority�, terminal load multiplied by 1.5
5. Terminal Load RTU will run in cooling mode until Zone 3 is satisfied (TL drops below 20%)
Zones 1 and 2 remain closed or in minimum position