Tympanic Membrane
430 likes | 984 Vues
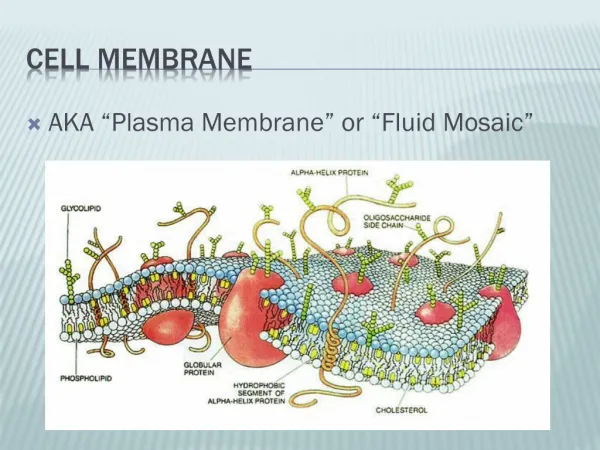
Tympanic Membrane. Tympanic Membrane. infant adult. EAM terminates at the tympanic membrane TM. In newborns the TM is horizontal In adults , the TM sits at a 55 degree angle. Ossification of EAM causes changes in angle of TM until about age 5 when it reaches adult position.

Tympanic Membrane
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Tympanic Membrane infant adult • EAM terminates at the tympanic membrane TM. • In newborns the TM is horizontal • In adults , the TM sits at a 55 degree angle. • Ossification of EAM causes changes in angle of TM until about age 5 when it reaches adult position.
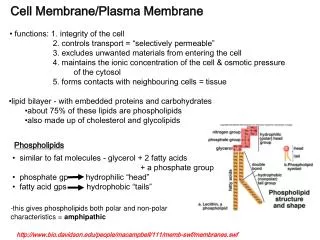
Tympanic Membrane • Very thin and translucent (wax paper). • Average thickness is 0.74 mm (.003 inches). • Elliptically shaped • Vertically .9 cm • Horizontally .8 cm
Tympanic Membrane • Three Layers of TM • Ectoderm (cutaneous) - continuous with EAM • Mesoderm (fibrous) • Radial Fibers • Concentric Fibers • Endoderm (mucous) - continuous with Tympanic Cavity. • Pars Tensa contains all three layers. • Pars Flacida DOES NOT contain fibrous layer.
Middle Ear • Tympanic Cavity • Ossicles • Eustachian Tube • Middle Ear Muscles
Tympanic Cavity • About same size/shape as an aspirin tablet. • 15 mm (superior to inferior) • 15 mm (anterior to posterior) • 5 mm (lateral to medial) • For descriptive purposes the TC has been compared to a six-sided room (4 walls + ceiling + floor).
Tegmen • Also known as the superior wall. • Paper thin. • Separates the tympanic cavity from the posterior cranial fossa which houses the temporal lobe. • Inflamatory conditions of middle ear can pass through the petrous-squamosal suture in children directly to the meninges of temporal lobe of cortex.
Jugular Wall • No landmarks. • Jugular vein is found inferior to this wall. • Glomus bodies can push up through this wall from jugular vein causing glomus jugularis.
Ossicles • Connects tympanic membrane with the oval window. • Smallest bones in the human body • Connected via a series of joints. • Held in place by a series of ligaments, tendons, and joints (see p. 455 of Zemlin).
Ossicular Chain • Function • Sound transmission to oval window • Protect cochlea from intense vibrations by changing axis of rotation of stapes.
Eustachian Tube • Function • Pressure equalization • Drainage • Description • 35 mm and drops at about a 40 degree angle. • Cartilaginous portion is 2/3, osseous portion is 1/3 • Osseous portion is open, Cartilaginous portion is usually closed. • Begins at tympanic cavity and terminates in nasopharynx.
Eustachian Tube • Function • Tensor palatini definitely involved in opening ET. • Levator palatini role is not clear. • Opening has been described as a milking action and also been described as the tensor palatini pulling on side of ET, opening the tube.
Eustachian Tube • Differences between adults and infants • Angle of ET • Adults - about 40 degrees • Children - more horizontal • Length • Adults - about 35 mm • Children - shorter • Flaccidity • More flaccid in children
Eustachian Tube • Cleft Palate • Normally fibers from tensor palatini and levator palatini insert into the velum. • In cleft palate fibers from these two muscles insert into the levator palatini may insert into hard palate and tensor palatini may insert into lateral portions of velum. • Number of fibers for these two muscles is often reduced in people with cleft palate.
Function of the middle ear • The middle ear system that includes the tympanic membrane and the ossicles, acts as an impedance matchingdevice between the air-borne sound waves and the fluids of the inner ear.
Function of the middle ear • Must consider tympanic membrane • Impedance … opposition to the flow of energy. • Impedance mismatch… occurs when you have two mediums of differing impedances. • Impedance mismatch occurs between gas (air) in environment and fluid of inner ear.
Areal Advantage • 17:1 (55:3) areal advantage between tympanic membrane and oval window and yields
Lever Advantage • 1.3:1 lever advantage
Resonance of the Middle Ear • The middle ear ear system creates a gain of nearly 30 dB between 1000 and 2000 Hz.
Resonance of the Middle Ear • Effects of increased mass and stiffness. • increase in mass causes downward shift of resonant frequency. • increase in stiffness causes upward shift in resonant frequency.