Periodic Table Information
70 likes | 142 Vues
Periodic Table Information. The Periodic Table of Elements is arranged in a way that allows chemists to make predictions about an elements’ physical and chemical characteristics .

Periodic Table Information
E N D
Presentation Transcript
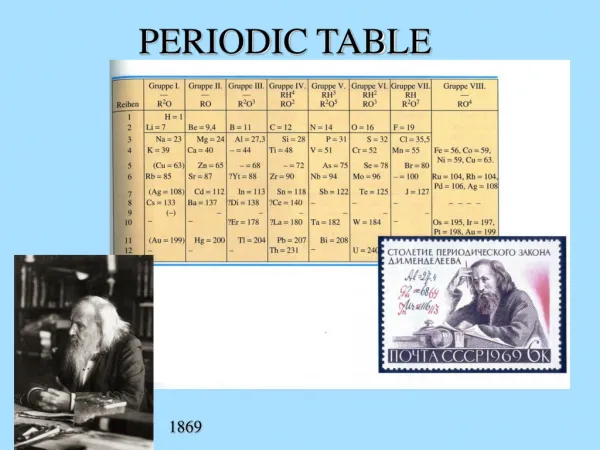
Periodic Table Information The Periodic Table of Elements is arranged in a way that allows chemists to make predictions about an elements’ physical and chemical characteristics. Dmitri Mendeleev was credited as the first (1869) to arrange the elements in their current format (increasing atomic mass). Henry Moseley later founded the Periodic Law (1913) and arranged the elements according to increasing atomic number.
The 115 known elements are organized by: • groups or families (vertical columns) that are similar in their chemical reactivity; having specific names. • periods (horizontal rows); that represent the number of occupied energy levels. Alkali Metals Alkaline Earth Metals Transition Metals Earth Metals (boron grp) Tetrels (carbon grp) Pnictogens (nitrogen grp) Chalcogens Halogens Noble Gases Lanthanides & Actinides
Metals and Non-metals are separated in the Periodic Table by the “staircase”. Metalloids (or semi-metals) are identified as any element that touches the staircase
Atomic Number: indicates number of protons for an atom of that element (and number of electrons for a neutral atom) Mass Number: indicates total number of protons and neutrons for an atom of that element • Number of Neutrons = Mass # - Atomic #
Isotopes are atoms that contain the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. eg: Radioisotopes are isotopes that are unstable and release energy in the form of alpha(a) or beta(b) particles or gamma(g) rays. They have many useful applications including medical diagnostics and radiation treatments.
Chemical Reactivity Bohr-Rutherford diagrams illustrate the arrangement of electrons in orbits around the nucleus (containing protons & neutrons). The family number of the element indicates the number of electrons in the outer most orbit (valence shell).
Lewis Symbols illustrate only the valence electrons of the element. Elements react in order to obtain a “full outer shell” of electrons, by either losing them to become a positive ion (cation) or gaining some to become a negative ion (anion), in the hope of becoming isoelectronic with the nearest Noble gas. This full complement of 8 electrons in an elements last orbit is known as the Octet Rule.